Karaka (कारकम्)
What is a Language ?
- What is the purpose of a language ?
- What is the fundamental unit of a language?
- What does a sentence in any language convey?
- Some sample sentences
- The boy is eating a banana.
- Ram went to school.
- Gowri is writing a letter with a pencil.
- Children are playing.
Sentence
- We observe that any sentence conveys some Action/’Activity.
- In Sanskrit it is called क्रिया
- Does the sentence convey only क्रिया ? What else ?
- We observe that entities associated with क्रिया are also conveyed.
- Does the sentence just list all the entities associated in the क्रिया ? What else ?
- The role of each entity in the क्रिया is also conveyed.
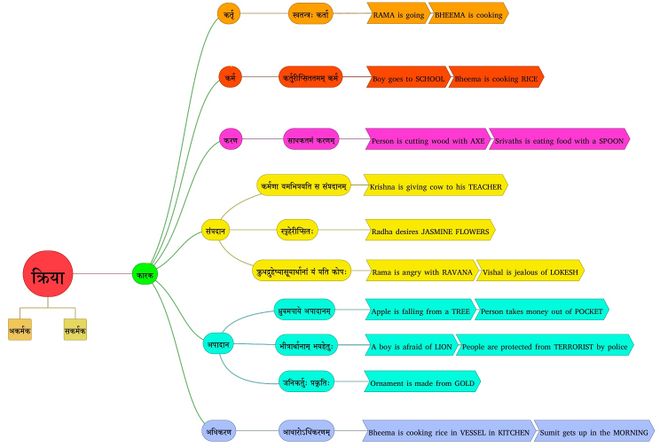
कारकम् ॥
- An entity that is participating in the क्रिया is called कारक
- For example in the sentence - The boy is eating a banana.
Can we list the entities that are associated in this क्रिया
Eg : Boy , Banana
- Similarly list down all the things/entities that are associated in the क्रिया , for each sentence we have written earlier.
- Each entity in the list is called a कारक
| Sr.no | Sentence | क्रिया | कारकऽ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A Student is reading a story | ||
| 2 | Joshi is singing a song | ||
| 3 | Vinay saw a movie in a theatre | ||
| 4 | Latha is talking to her
son on mobile |
कारकप्रभेदाः ॥
कर्तृकारक
- Depending on its role in क्रिया, कारक is classified into different types
- What is the most essential entity required for क्रिया to happen ?
- The Doer ? The one who performs/initiates the क्रिया.
- This type of कारक is called कर्तृकारक
Identify the कर्तृकारक in the sample sentences written
| Sr.no. | Sentence | क्रिया | कर्तृ-कारक |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vishnu went to school | ||
| 2 | Shiva is eating an apple | ||
| 3 | Kumar is sleeping on a bed | ||
| 4 | Prasad is cooking dal in
a Vessel |
The main सूत्र that defines कर्तृकारक is
स्वतन्त्रः कर्ता (१-४-५४) - The entity that initiates/performs the क्रिया is called कर्तृकारक. Generally we can observe the क्रिया happening in this कर्तृ-कारक.
कर्मकारक
- What is the intention/objective of कर्तृ in performing the क्रिया ? How long does the क्रिया happen ?
The intention/objective of the कर्तृ is to create an entity or make a change in some entity. The क्रिया will happen till the objective is met.
- The entity (कारक) that is created or undergoes a change after doer/कर्तृ performs the क्रिया acting upon it is called कर्मकारक. These are few types we can consider -
निर्वत्र्य - ewly created
विकार्य - transformed
प्राप्य -reached /understood
The main सूत्र that defines कर्मकारक is -
कर्तुरीप्सिततमं कर्म (१-४-४९) - The entity in which the कर्तृ intends to obtain his objective by performing the क्रिया is called कर्मकारक
| Sr.no. | Sentence | क्रिया | कर्म-कारक |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vishnu went to school | ||
| 2 | Shiva is eating an apple | ||
| 3 | Kumar is sleeping on a bed | ||
| 4 | Prasad is cooking dal in
a Vessel |
अधिकरणकारक
- We have seen that the क्रिया performer is कर्तृ-कारक and acted upon is कर्म-कारक, but what is the substratum for कर्तृ, कर्म ?
- The entity (कारक) that is the substratum for कर्तृ or कर्म is called अधिकरणकारक
Eg : In the kitchen, Bhima is cooking rice in a vessel.
- Here kitchen is substratum/ आश्रय for Bhima(कर्तृ) , and Vessel is substratum/ आश्रय for rice (कर्म) .
Hence both kitchen and vessel are अधिकरणकारकऽ
Time and space are अधिकरणकारकऽ for any क्रिया.
The locus of interest for our mental faculties or the subject matter of a text is also called अधिकरणकारक. This is technically called विषय.
Eg: He is interested in व्याकरण , here व्याकरण is अधिकरणकारक
He has devotion in God , here God is अधिकरणकारक
The main सूत्र that defines अधिकरणकारक is
आधारोऽधिकरणम् (१-४-४५) - The entity which is substratum (आधार) for कर्तृकारक or कर्मकारक is called अधिकरणकारक
करणकारक
- In some क्रिया, tools/instruments are used.
- The entity (कारक) that is a tool/instrument is called करणकारक
- Definition of instrument ?
There should be a transfer of action from कर्तृ to the tool, in turn that tool should generate/achieve the desired result for the कर्तृ .
Eg : Wood-cutter performs an action of chopping, he transfers his action to the axe , the axe chops the wood. The कारक axe is called is करणकारक.
The main सूत्र that defines करणकारक is
साधकतमं करणम् (१-४-४२) - The most important tool/instrument(साधक) in performing the क्रिया is ca11ed करणकारक
सम्प्रदानकारक
- In the act of giving, the receiver is सम्प्रदानकारक
Eg : Krishna gives a cow to his teacher. Here सम्प्रदानकारक is the teacher
- In the act of desiring, the entity that is desired is सम्प्रदानकारक
Eg : Radha desires jasmine flower. Jasmine flower is सम्प्रदानकारक
- In the act of getting angry, the person/entity towards whom he is angry at is सम्प्रदानकारक
Eg: Rama is angry towards Ravana. सम्प्रदानकारक is Ravana
The सूत्रऽ that define सम्प्रदानकारक are
- कर्मणा यमभिप्रैति स सम्प्रदानम् (१-४-३२) - In the act of giving, कर्तृ gives the कर्मकारक to a receiver, the receiver is called सम्प्रदानकारक
- स्पृहेरीप्सितः (१-४-३६) - n the act of desiring, कर्तृ desires to have something, this desired entity is called सम्प्रदानकारक
- क्रुधद्रुहेर्ष्यऽसूयार्थानां यं प्रति कोपः । (१-४-३७) - the act of getting angry, deceiving, having grudge, envying, कर्तृ is angry towards someone, this person/entity towards whom कर्तृ is angry called सम्प्रदानकारक
अपादानकारक
- In the act of separation, the reference entity from which the separation happens is अपादानकारक. Eg : Fruit is falling from tree. Fruit is separated from tree. अपादानकारक is the Tree
- In the act of fearing/protecting, the one Who causes fear is अपादानकारक. Eg : 1. Boy is afraid of lion. अपादानकारक is Lion. 2. People are protected from terrorist. अपादानकारक is terrorist.
- In the act of being born, the source/raw material is अपादानकारक. Eg : Plant is born out of seed. अपादानकारक is the Seed.
The सूत्रऽ that define अपादानकारक are
- ध्रुवमपायेऽपादानम् (१-४-२४) - In the act of separation, कर्तृ get separated from a reference entity, that reference entity is called अपादानकारक
- भीत्रार्थानां भयहेतुः (१-४-२५) - । the act of getting afraid or protection, कर्तृ is having fear from someone, that person/entity that is the cause of fear is called अपादानकारक
- जनिकर्तुः प्रकृतिः । (१-४-३०) - In the act being born, the कर्तृ is born out of some raw material/source, this raw material/source is called अपादानकारक
क्रियाप्रभेदः ॥
अकर्मक/सकर्मक-क्रिया
- For any क्रिया, will there be always a necessity to have another entity to act upon (कर्मकारक)? If possible, find क्रियाऽ that does not need कर्मकारक
- क्रिया which DOES NOT require any other entity to act upon, that is the क्रिया that DOES NOT require a कर्मकारक is called अकर्मक-क्रिया
Eg : Sleeping, Running, Laughing, Sitting etc
- क्रिया which requires an entity to act upon or transform some entity, i.e., the क्रिया that needs कर्मकारक is called सकर्मक-क्रिया
Eg : Eating, Seeing, Cooking, Hearing, Chopping etc
द्विकर्मक
In certain types of actions there will be one more कारक which was not classified or defined. That has to be considered as कर्मकारक . (अकथितं च १/४/५१) ।
० Eg : देवदत्तः माणावकं पन्थानं पृच्छति ।
० पुरुषः पौरवं गां याचते ।
० गोपालकः गां दोग्धि पयः ।
These are found only the following धातुऽ and in their meaning -
दुहँ प्रपूरणे, टुयाचृँ याच्ञायाम्, डुपचँष् पाके, दन्ड दण्डनिपाते, रुधिँर् आवरणे , प्रछँ ज्ञीप्सायाम्, भिक्षँ भिक्षायामलाभे लाभे च, चिञ् चयने, ब्रूञ् व्यक्तायां वाचि, शासुँ अनुशिष्टौ, जि जये अभिभवे च, मथिँ विलोडने, मुषँ स्तेये, णीञ् प्रापणे, वहँ प्रापणे, हृञ् हरणे, कृषँ विलेखने, भाषँ व्यक्तायां वाचि
द्विकर्मक Examples
अविनीतं विनयं याचते ।
तण्डुलान् ओदनं पचति ।
गर्गान् शतं दण्डयति ।
व्रजम् अवरुणद्धि गाम् ।
वृक्षम् अवचिनोति फलानि ।
माणवकं धर्मं ब्रूते शास्ति वा ।
शतं जयति देवदत्तम् ।
सुधां क्षीरनिधिं मथ्नाति ।
देवदत्तं शतं मुष्णाति ।
ग्राममजां नयति हरति कर्षति वहति वा ।
कारकसूत्राणि ॥
सूत्रऽ (अध्यायः - १, पादः - ४ , सूत्रं -२३-५५)
- कर्तृ-कारक - स्वतन्त्रः कर्ता (१-४-५४)
- कर्म-कारक - कर्तुरीप्सिततं कर्म (१-४-४९)
- अधिकरण-कारक - आधारोऽधिकरणम् (१-४-४५)
- करण-कारक : साधकतमं करणं (१-४-४२)
- सम्प्रदान-कारक - कर्मणा यमभिप्रैति स सम्प्रदानम् (१-४-३२) स्पृहेरीप्सितः (१-४-३६) क्रुधद्रुहेर्ष्याऽसूयार्थानां यं प्रति कोपः(१-४-३७)
- अपादान-कारक - ध्रुवमपायेऽपादानम् (१-४-२४) भीत्रार्थानां भयहेतुः (१-४-२५) जनिकर्तुः प्रकृतिः (१-४-३०)