Difference between revisions of "Kalamana (कालमानम्)"
(added content and reference) |
(added content and references) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ToBeEdited}} | {{ToBeEdited}} | ||
| − | Kalamana (Samskrit: कालमानम्) broadly refers to the measurement of time (Kala). Bharatiya shastrajnas have explained the various macrocosmic and microcosmic time systems and depending on the needs of particular topics in astronomy, different scales and units of time are used. On the macrocosmic scale, the Yuga system has been described, whereas on the microcosmic scale, a small unit of time Truti (1/33750 of a second) has been mentioned by Bhaskara II. We mention the macrocosmic time scales (Svetavaraha kalpa, Vaivasvata Manvantara etc) only in the samkalpa of our daily puja rituals. | + | Kalamana (Samskrit: कालमानम्) broadly refers to the measurement of time ([[Kala (कालः)|Kala]]). Bharatiya shastrajnas have explained the various macrocosmic and microcosmic time systems and depending on the needs of particular topics in astronomy, different scales and units of time are used. On the macrocosmic scale, the Yuga system has been described, whereas on the microcosmic scale, a small unit of time Truti (1/33750 of a second) has been mentioned by Bhaskara II. We mention the macrocosmic time scales (Svetavaraha kalpa, Vaivasvata Manvantara etc) only in the samkalpa of our daily puja rituals.<ref name=":2" /> |
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Many of these factors are based on simple natural observations, earth, moon and planetary motions and seasons - all of which are pratyaksha pramanas (visible evidence) in the nature around us manifesting the environmental changes. It is common knowledge that it is a day with sunrise, a night with sunset, high and low tides with lunar movements, rashis associated with the movement of moon in nakshatras, formation of new leaves and leaf shedding indicates seasonal change with Vishvat (equinoxes) so on and so forth. | Many of these factors are based on simple natural observations, earth, moon and planetary motions and seasons - all of which are pratyaksha pramanas (visible evidence) in the nature around us manifesting the environmental changes. It is common knowledge that it is a day with sunrise, a night with sunset, high and low tides with lunar movements, rashis associated with the movement of moon in nakshatras, formation of new leaves and leaf shedding indicates seasonal change with Vishvat (equinoxes) so on and so forth. | ||
| − | It is only with deep respect for the intellect and keen observation of our ancient maharshis, rsis and later day ganita and jyotisha shastrajnas that we can appreciate the systematic work done by them - not requiring huge telescopes or light measuring instruments - to leave a legacy of astronomical wealth for us. | + | It is only with deep respect for the intellect and keen observation of our ancient maharshis, rsis and later day [[Ganita Shastra (गणितशास्त्रम्)|ganita]] and jyotisha shastrajnas that we can appreciate the systematic work done by them - not requiring huge telescopes or light measuring instruments - to leave a legacy of astronomical wealth for us. |
Here we discuss a few important astronomical concepts, briefly, that are in use in our present day calendars, without delving deep into the mathematical calculations used to arrive at them. | Here we discuss a few important astronomical concepts, briefly, that are in use in our present day calendars, without delving deep into the mathematical calculations used to arrive at them. | ||
== नवमानानि ॥ Nine Kinds of Time == | == नवमानानि ॥ Nine Kinds of Time == | ||
| − | Surya Siddhanta is one of the oldest and accepted by many scholars as an authentic source of information regarding the astronomical calculations and specifications. | + | Surya Siddhanta is one of the oldest texts and accepted by many scholars as an authentic source of information regarding the astronomical calculations and specifications. Manaadhyaya (14th Adhyaya) of Surya Siddhanta is referred here to understand the different kinds of Kala that we use in day to day lives.<blockquote>ब्राह्मम् दिव्यम् तथा पित्र्यम् प्राजापत्यम् गुरोस् तथा । सौरम् च सावनम् चान्द्रम् आर्क्षम् मानानि वै नव ॥</blockquote><blockquote>चतुर्भिर्व्यवहारोऽत्र सौरचान्द्रार्क्षसावनैः।बार्हस्पत्येन षष्ट्यब्दा ज्ञेया नान्यैस्तु नित्यशः॥ (Sury. Sidd. 14.1-2)<ref name=":0">Surya Siddhanta ([https://sa.wikisource.org/wiki/%E0%A4%B8%E0%A5%82%E0%A4%B0%E0%A5%8D%E0%A4%AF%E0%A4%B8%E0%A4%BF%E0%A4%A6%E0%A5%8D%E0%A4%A7%E0%A4%BE%E0%A4%A8%E0%A5%8D%E0%A4%A4_%E0%A4%AE%E0%A4%BE%E0%A4%A8%E0%A4%BE%E0%A4%A7%E0%A5%8D%E0%A4%AF%E0%A4%BE%E0%A4%AF%E0%A4%83 Adhyaya 14])</ref></blockquote>There are nine Manas or measurements of time (kinds of time). They are |
# ब्राह्मम् ॥ Braahmam (Of Brahma) | # ब्राह्मम् ॥ Braahmam (Of Brahma) | ||
# दिव्यम् ॥ Divyam (Of Devatas) | # दिव्यम् ॥ Divyam (Of Devatas) | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
# चान्द्रम् ॥ Of Chandra | # चान्द्रम् ॥ Of Chandra | ||
# आर्क्षम् (नाक्षत्रम्) ॥ Aarksham (Of Nakshatra) | # आर्क्षम् (नाक्षत्रम्) ॥ Aarksham (Of Nakshatra) | ||
| − | The Manas which are used in daily activities are four in number - सौरचान्द्रार्क्षसावनैः । Solar, Lunar, Sidereal, and the Savana (Civil). The Mana of Jupiter (Barhaspatya) is used for determining the Shasthtyabda (60 Samvatsaras) or | + | The Manas, measures of time, which are used in daily activities are four in number - सौरचान्द्रार्क्षसावनैः । Solar, Lunar, Sidereal, and the Savana (Civil). The Mana of Jupiter (Barhaspatya) is used for determining the Shasthtyabda (60 Samvatsaras) or calculation of how a person attains 60 years of age. The remaining four Manas are not used for daily activities.<ref name=":1">Pt Mahavir Prasad Srivastav (1940 First Edition) ''Surya Siddhanta with Vijnana Bhashya, Parts 1 and 2.'' Allahabad: Dr. Ratnakumari Svadhyaya Sansthan. (Page 794 -)</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | While Suryasiddhanta is an astronomical text which is fundamentally a scientific treatise, Dharmashastra Nibandha texts such as Dharmasindhu and Nirnaya Sindhu also help us in determining the different Manas and lays down the vidhis associated with them. According to Dharmasindhu<blockquote>तत्र कालः षड्विधः ॥ वत्सरः अयनम् ऋतुर्मासः पक्षो दिवस इति॥ (Dharm. Sind.1)<ref name=":3">The Dharmasindhu by Kasinath Upadhyaya (1986 Reprint Edition) Delhi: Sri Satguru Publications (Pages 1-7)</ref></blockquote>Kala is of six kinds. Vatsara (वत्सरः) - one year, Ayanam (अयनम्) - half of a year or six months, Rtu (ऋतुः) - one season or two months, Masa (मासः) - one month or 30 days, Paksha (पक्षः) - one fortnight or 15 days, and Divasa (दिवसः) - one day. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It may be noted that the six kinds of time mentioned in Dharmasindhu are discussed in Suryasiddhanta also. | ||
== सौरमानम् ॥ Saura Mana == | == सौरमानम् ॥ Saura Mana == | ||
| − | It is long known to our ancient seers that it is the earth that revolves around the sun in an ecliptic path. However, the time is calculated based on using the earth as a reference, and thus we say sun is revolving around the earth. We see in the sky that due to diurnal motion, the Sun rises in the eastern horizon, moves up in the sky westward and sets in the western horizon. From the sunset to the next sunrise, it will be below the horizon during the night. It is common knowledge all over the world that this period of time between the sunrise and sunset is called a Day. However, our seers have calculated and defined a Day, not just with respect to the Earth but also with other cosmic references and specified where such a measure of time is to be used. | + | It is long known to our ancient seers that it is the earth that revolves around the sun in an ecliptic path. However, the time is calculated based on using the earth as a reference, and thus we say sun is revolving around the earth. We see in the sky that due to the diurnal motion, the Sun rises in the eastern horizon, moves up in the sky westward and sets in the western horizon. From the sunset to the next sunrise, it will be below the horizon during the night. It is common knowledge all over the world that this period of time between the sunrise and sunset is called a Day. However, our seers have calculated and defined a Day, not just with respect to the Earth but also with other cosmic references and specified the purpose where such a measure of time is to be used. |
| − | + | === सौरदिनम् ॥ Saura Dina (Solar Day) === | |
<blockquote>सौरेण द्युनिशोर्मानं षडशीतिमुखानि च। अयनं विषुवच्चैव सम्क्रान्तेः पुण्यकालता॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.3)<ref name=":0" /></blockquote>With reference to Earth the Sun's motion along the ecliptic path, in the rashi, is about 1° per day. This is called a Solar Day. | <blockquote>सौरेण द्युनिशोर्मानं षडशीतिमुखानि च। अयनं विषुवच्चैव सम्क्रान्तेः पुण्यकालता॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.3)<ref name=":0" /></blockquote>With reference to Earth the Sun's motion along the ecliptic path, in the rashi, is about 1° per day. This is called a Solar Day. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 38: | ||
There are four Shadasheeti Mukhas in a year. <blockquote>तुलादि षडशीत्यह्नाम् षडशीतिमुखम् क्रमात् । तच्चतुष्टयम् एव स्याद् द्विस्वभावेषु राशिषु ॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.4)</blockquote>Every eighty-sixth solar day reckoned from the time of Tula Sankramana (Day the Sun enters Tula rashi) is called Shadasheeti Mukha in succession. They are four in number and happen when Sun is in 4 Dvisvabhava Rashis, namely Dhanas (26°of Saggitarius), Meena (22° of Pisces), Mithuna (18° of Gemini) and Kanya (14° of Virgo) rashis. | There are four Shadasheeti Mukhas in a year. <blockquote>तुलादि षडशीत्यह्नाम् षडशीतिमुखम् क्रमात् । तच्चतुष्टयम् एव स्याद् द्विस्वभावेषु राशिषु ॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.4)</blockquote>Every eighty-sixth solar day reckoned from the time of Tula Sankramana (Day the Sun enters Tula rashi) is called Shadasheeti Mukha in succession. They are four in number and happen when Sun is in 4 Dvisvabhava Rashis, namely Dhanas (26°of Saggitarius), Meena (22° of Pisces), Mithuna (18° of Gemini) and Kanya (14° of Virgo) rashis. | ||
| − | ==== Pitrpaksha ==== | + | ==== पितृपक्षम् ॥ Pitrpaksha ==== |
<blockquote>ततः शेषाणि कन्याया यान्य् अहानि तु षोडश । क्रतुभिस् तानि तुल्यानि पितृऋणाम् दत्तम् अक्षयम् ॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.6)</blockquote>After the 4th Shadasheethi Mukha (in Kanya), the remaining 16 solar days of the solar month when Sun is in Kanya rashi are equivalent to the time of Yajna, (kala when any good actions give great merit) and in these days dana offered to Pitrs will give infinite merit.<ref>Pt. Bapu Deva Sastri (1861) ''Translation of the Surya Siddhanta and Revision of Siddhanta Siromani Translated by Lancelot Wilkinson.'' Calcutta: Asiatic Society. (Pages 91-)</ref> | <blockquote>ततः शेषाणि कन्याया यान्य् अहानि तु षोडश । क्रतुभिस् तानि तुल्यानि पितृऋणाम् दत्तम् अक्षयम् ॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.6)</blockquote>After the 4th Shadasheethi Mukha (in Kanya), the remaining 16 solar days of the solar month when Sun is in Kanya rashi are equivalent to the time of Yajna, (kala when any good actions give great merit) and in these days dana offered to Pitrs will give infinite merit.<ref>Pt. Bapu Deva Sastri (1861) ''Translation of the Surya Siddhanta and Revision of Siddhanta Siromani Translated by Lancelot Wilkinson.'' Calcutta: Asiatic Society. (Pages 91-)</ref> | ||
| − | From this we understand that, Shraddha for Pitrs should happen when Sun is in Kanya rashi starting from 15° to 30° according to Saura Mana. However, in the present times, Saura Mana is not used. According to Purnimanta system, Krishna paksha of Ashvini month (dark half of month of Ashvini) and according to | + | From this we understand that, Shraddha for Pitrs should happen when Sun is in Kanya rashi starting from 15° to 30° according to Saura Mana. However, in the present times, Saura Mana is not used. According to Purnimanta system, Krishna paksha of Ashvini month (dark half of month of Ashvini) and according to Amanta system, Krishna paksha of Bhadrapada month (dark half of the month of Bhadrapada) i.e., calculated according to Chandra Mana are the days of Pitrpaksha followed by people.<ref name=":1" /> |
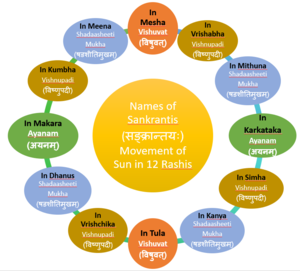
| − | ==== | + | ==== सङ्क्रान्तयः ॥ Sankrantis ==== |
| − | <blockquote>भचक्रनाभौ विषुवद्द्वितीयं समसूत्रगम् । अयनद्वितयं चैव चतस्रः प्रथितास्तु ताः॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.7)</blockquote> | + | [[File:Names of Sankrantis.PNG|thumb|474.556x474.556px|Names of 12 Sankrantis]] |
| − | + | The time at which Sun enters into an new rashi is termed Sankranti. <blockquote>भचक्रनाभौ विषुवद्द्वितीयं समसूत्रगम् । अयनद्वितयं चैव चतस्रः प्रथितास्तु ताः॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.7)</blockquote>In the middle of the nakshatra chakra (sphere of stars) the two equinoxes (Vishuvats in Mesha and Tula rashis) are diametrically opposed and so are the two solistices (Ayanas in Karkataka and Makara) in the ecliptic path. | |
| − | ==== Purpose of Saura Dina | + | The Shadasheeti Mukhas happen when Sun moves in the four rashis namely, Mithuna, Kanya, Dhanus, and Meena as described above (Surya. Siddhanta 14.4), the remaining four sankrantis (in Vrishabha, Simha, Vrschika and Kumbha) are called Vishnupadi. |
| + | |||
| + | ==== उत्तरायणम् दक्षिणायनम् च॥ Uttarayana and Dakshinayana ==== | ||
| + | <blockquote>तयोर्मकरसङ्क्रान्तेः षण्मासेषूत्तरायणम् । कर्क्यादेस्तु तथैव स्यात् षण्मासा दक्षिणायनम् ॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.9)</blockquote>From the time Sun enters Makara rashi (Capricorn) the six months are termed Uttarayana (northern movement of the Sun); in the same manner from the time Sun enters Karkataka (Cancer), the six solar months are called Dakshinayana (southern movement of the Sun).<ref name=":1" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Purpose of Saura Dina === | ||
# Determining the length of the day and night | # Determining the length of the day and night | ||
# Shadashiiti Mukhas | # Shadashiiti Mukhas | ||
# Determine Uttarayana and Dakshinayana (the northern and southern paths of the Sun) | # Determine Uttarayana and Dakshinayana (the northern and southern paths of the Sun) | ||
| − | # Equinoxes and Vishuvats | + | # Equinoxes and Solistices (Vishuvats etc) |
# Sankrantis (the time of entry of Sun into a new rashi) | # Sankrantis (the time of entry of Sun into a new rashi) | ||
| − | === सौरमासं सौरवर्षं च ॥ Solar | + | === सौरमासं सौरवर्षं च ॥ Solar Month and Year === |
| − | The time taken by the Sun to complete a revolution (360°) around the Earth, as observed from the Earth, is defined as a Saura Varsha (Solar Year) | + | <blockquote>द्विराशिनादृतवः षदुक्ताशिशिरादयः । मेषादयो द्वादशैते मासास्तैरेव वत्सरः ॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.10)</blockquote>Six Seasons are formed covering the time when Sun moves in two signs in a cyclic manner; Shishira (very cold season) is said to occur for two months when Sun enters Makara rashi and rest of the Rtus occur successively for two months. Starting from the Mesha rashi, the movement of Sun along the 12 rashis (returning back to Mesha rashi) in 12 months constitutes a Solar Year. |
| + | |||
| + | Dharmasindhu refers to the above explanation of the solar year as follows<blockquote>मेषादिषु द्वादशराशिषु रविभुक्तेषु पञ्चषष्ट्यधिकशतत्रयदिनैः सौरवत्सरः संपद्यते ॥ (Dhar. Sind. 1)<ref name=":3" /></blockquote>Therefore, a solar month is the time taken by the Sun to cover a rashi (30°) along the ecliptic path.<ref name=":1" /><ref name=":2" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The time taken by the Sun to complete a revolution (360°) around the Earth, as observed from the Earth, is defined as a Saura Varsha (Solar Year). To complete the 360° revolution the Sun takes about 365.25 Savana or Civil days.<ref name=":2" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Sayana and Nirayana Solar Years ==== | ||
| + | As mentioned above Solar years refer to Sun's revolution, as observed from the Earth. However, depending on the points of reference chosen, we have two different types of solar years | ||
| + | # Nirayana or Sidereal Solar Year | ||
| + | # Sayana or Tropical Solar Year | ||
| + | '''Nirayana (Sidereal) Saura varsha''' is the time taken by the Sun to complete a revolution, along the ecliptic path, with reference to a fixed star. Careful observations carried out over a long time enabled our ancient astronomers to determine the duration of a Nirayana Solar Year as 365.256364 days (365 Days, 6 Hours, 9 Minutes, 9.8 secs). | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Sayana (Tropical) Saura varsha''' is the time taken by the Sun to complete a revolution, along the ecliptic path, with reference to the Vishuvat in Mesha (Vernal equinox). This time has been determined to be equal to 365.242190 (365 Days, 5 Hours, 48 Minutes and 46 secs). It is this Sayana Saura varsha that determines seasons.<ref name=":2" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Summary === | ||
| + | '''1 Saura Dina (Solar Day) = Movement of Sun in a Rashi by 1° in ecliptic path''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''1 Saura Masa (Solar Month) = Movement of the Sun across one Rashi (30°) in ecliptic path = 30.43803 days''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''1 Saura Varsha (Solar Year) = 365.25 Savana or Civil days''' | ||
== सावनमानम् ॥ Savana Mana == | == सावनमानम् ॥ Savana Mana == | ||
=== सावनदिनम्॥ Savana Dina (Civil Day) === | === सावनदिनम्॥ Savana Dina (Civil Day) === | ||
| − | <blockquote>उदयाद् उदयम् भानोः सावनम् तत् प्रकीर्त्यते । सावनानि स्युरेतानि यज्ञकालविधिस्तु तैः ॥ </blockquote><blockquote>सूतकादिपरिच्छेदो दिनमासाब्दपास्तथा । मध्यमा ग्रहभुक्तिस्च सावनेन प्रकीर्त्यते ॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.18)<ref name=":0" /></blockquote>The duration between two successive risings of the Sun is called a Savana Dina or Civil Day.<ref name=":1" /> | + | <blockquote>उदयाद् उदयम् भानोः सावनम् तत् प्रकीर्त्यते । सावनानि स्युरेतानि यज्ञकालविधिस्तु तैः ॥ </blockquote><blockquote>सूतकादिपरिच्छेदो दिनमासाब्दपास्तथा । मध्यमा ग्रहभुक्तिस्च सावनेन प्रकीर्त्यते ॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.18-19)<ref name=":0" /></blockquote>The duration between two successive risings of the Sun is called a Savana Dina or Civil Day.<ref name=":1" /> |
Observations of sunrise over a very long time has revealed that the duration of a day is not constant but varies from day to day although very slightly. An average calculated based on the observations is referred to as the Mean Solar Day or Mean Civil day. Savana Dina is divided into 60 equal parts called Ghatikas or 24 equal parts called Hora (hours). Thus the 24 hour day that is used for our regular daily activities is the Savana Dina.<ref name=":2">Rao, S. Balachandra. (2000) ''Indian Astronomy, An Introduction.'' Hyderabad: Universities Press (India) Limited. (Page 39-50)</ref> | Observations of sunrise over a very long time has revealed that the duration of a day is not constant but varies from day to day although very slightly. An average calculated based on the observations is referred to as the Mean Solar Day or Mean Civil day. Savana Dina is divided into 60 equal parts called Ghatikas or 24 equal parts called Hora (hours). Thus the 24 hour day that is used for our regular daily activities is the Savana Dina.<ref name=":2">Rao, S. Balachandra. (2000) ''Indian Astronomy, An Introduction.'' Hyderabad: Universities Press (India) Limited. (Page 39-50)</ref> | ||
| − | '''1 Savana Day (Civil Day) = 24 Hours''' | + | '''1 Savana Day (Civil Day) = 60 Ghatikas = 24 Hours''' |
==== Purpose of Savana Dina ==== | ==== Purpose of Savana Dina ==== | ||
| Line 71: | Line 99: | ||
=== तिथिः ॥ Tithi (Lunar Day) === | === तिथिः ॥ Tithi (Lunar Day) === | ||
| − | <blockquote>अर्काद्विनिस्सृतः प्राचीं यद्यात्यहरहश्शशी। तच्चान्द्रमानम् अम्शैस्तु ज्ञेया द्वादशभिस्तिथिः॥ </blockquote><blockquote>तिथिः करणम् उद्वाहः क्षौरम् सर्वक्रियास् तथा। व्रतोपवासयात्राणाम् क्रिया चान्द्रेण गृह्यते॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.12-13)<ref name=":0" /></blockquote>The time in which the Moon being separate from the Sun (after a conjunction) moves daily to the east is the measurement for the moon (चान्द्रमानम्) Chandra Mana. The time taken by the Moon to cover exactly | + | <blockquote>अर्काद्विनिस्सृतः प्राचीं यद्यात्यहरहश्शशी। तच्चान्द्रमानम् अम्शैस्तु ज्ञेया द्वादशभिस्तिथिः॥ </blockquote><blockquote>तिथिः करणम् उद्वाहः क्षौरम् सर्वक्रियास् तथा। व्रतोपवासयात्राणाम् क्रिया चान्द्रेण गृह्यते॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.12-13)<ref name=":0" /></blockquote>The time in which the Moon being separate from the Sun (after a conjunction) moves daily to the east is the measurement for the moon (चान्द्रमानम्) Chandra Mana. The time taken by the Moon to cover exactly a distance of 12° relative to the Sun, is defined as Tithi or Lunar Day.<ref name=":1" /> |
| + | |||
| + | The Moon, like the Sun, moves from west to east with reference to the fixed stars. Since the moon moves faster than the sun, starting from a new moon, the moon gains about 12° per day over the Sun, i.e., one Tithi per day, thus the chandra masa has 30 tithis. The half-lunar month from a new moon to the succeeding full moon is called Shukla Paksha (the bright fortnight) and the other half-lunar month from the full moon to next new moon is called Krshna Paksha (dark fortnight). The lunar month is a natural unit for a month. It is important to note that the beginning and end of a lunar month are naturally marked by two successive new moons.<ref name=":2" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Sidereal Period of Moon === | ||
| + | The moon moves along its own orbit, with a slight inclination towards the ecliptic path. It is found that the moon takes an average period of 27.32166 days to complete a revolution with reference to the fixed stars. This time interval is called the Sidereal Period of Moon, since the moon takes this much time to complete an angular revolution of 360°, its motion per day is given as 360/27.32166 = 13°10'. In comparison to this, the sun's motion along the ecliptic, in the same direction, is about 1° per day. Thus the moon overtakes the Sun by about 12°10' per day.<ref name=":2" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === चन्द्रमासं चन्द्रवर्षं च ॥ Lunar Month and Year === | ||
| + | If the Sun and Moon are moving in the same direction, in which case their celestial longitude is the same, as seen from the Earth, the moon is said to be "new" or it is called Amavasya or New Moon Day. After 24 hours the moon would have moved ahead of the Sun by about 12°10'. This increasing separation of the moon from the sun goes on at the rate of 12°10' per day until it reaches 360°. At this point the moon will be in conjunction (or in the same direction) as the sun, resulting in a new moon. The interval between two successive new moons is called the synodic period of the Moon ("synodic" means successive conjunctions of the same bodies). This synodic period of the Moon is defined as a Lunar month (Chandra Masa). Thus one lunar month = 29.530589 days (29 Days, 12 Hours, 44 Minutes, and 2.9 secs).<ref name=":2" /> | ||
| − | + | Dharmasindhu elaborates about the course of a lunar month, when the Moon goes through a cycle of phases, from new moon to full moon and then to new moon again. <blockquote>शुक्लप्रतिपदादिदर्शांन्तैश्चैत्रादिसंज्ञैर्द्वादशभिर्मासैश्चतुःपञ्चाशदधिकशतत्रयदिनैः सति मलमासे त्रयोदशभिर्मासैश्चान्द्रो वत्सरः॥ (Dhar. Sind. 1)<ref name=":3" /></blockquote>From the Shukla Pratipat tithi till the end of Amavasya, there are 30 tithis; together they constitute one Chandra-masa or Lunar month namely Chaitra, etc. 12 such Lunar months make up a Lunar Year having 354 days (savana days). When an Adhika masa is present there are 13 months a lunar year. | |
| − | + | === Purpose of Chandra Mana === | |
# Determination of Tithi, Karana (half of Tithi) | # Determination of Tithi, Karana (half of Tithi) | ||
| − | # Determine the time for samskaras like marriage | + | # Determine the auspicious time for samskaras like marriage |
# Determine the appropriate time for activities such as shaving, tonsure | # Determine the appropriate time for activities such as shaving, tonsure | ||
# To determine the time for Vratas, Upavasas, Yatras | # To determine the time for Vratas, Upavasas, Yatras | ||
| + | '''1 Tithi (Lunar Day) = Time taken by the Moon to cover a distance of 12° relative to the Sun''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''1 Chandra Masa (Lunar Month) = 29.530589 days''' | ||
== नाक्षत्रमानम् ॥ Nakshatra Mana == | == नाक्षत्रमानम् ॥ Nakshatra Mana == | ||
=== नाक्षत्रदिनम् ॥ Nakshatra Dina (Sidereal Day) === | === नाक्षत्रदिनम् ॥ Nakshatra Dina (Sidereal Day) === | ||
| − | <blockquote>भचक्रभ्रमणम् नित्यम् नाक्षत्रम् दिनम् उच्यते। नक्षत्रनाम्ना मासास् तु ज्ञेयाः पर्वान्तयोगतः ॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.15)<ref name=":0" /></blockquote>The time taken for one revolution of the sphere of stars is called a sidereal day. | + | <blockquote>नाडी षष्ट्या तु नाक्षत्रमहोरात्रं प्रकीर्तितम् । तत्त्रिम्शता भवेन्मासः सावनोऽर्कोदयैःस्मृतः॥ (Sury. Siddh. 1.12)</blockquote>The time which contains sixty ghatikas is called a Nakshatra Ahoratra (a sidereal day and night) or Day and a Nakshatra masa (a sidereal month) consists of thirty Nakshatra Ahoratras. <blockquote>भचक्रभ्रमणम् नित्यम् नाक्षत्रम् दिनम् उच्यते। नक्षत्रनाम्ना मासास् तु ज्ञेयाः पर्वान्तयोगतः ॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.15)<ref name=":0" /></blockquote>The time taken for one revolution of the sphere of stars is called a sidereal day. The time taken by the fixed stars to go around the earth is called a Nakshatra Dina or Sidereal Day; and this time is equal to the period of the rotation of the Earth. |
| − | + | Sidereal is a term used to refer to stars. It is important to note that the time taken by the fixed stars to go round the Earth once is not the same as that taken by the Sun. While all the celestial bodies appear to move from the east to west due to the diurnal motion, the Sun would have moved from west to east along the ecliptic by about 1°, relative to the stars. Therefore, the fixed stars take a little less than 24 hours (mean civil day) to complete a rotation around the Earth. As a natural consequence if a particular star rises in the eastern horizon at a particular time today, it will rise about two hours earlier after 30 days, 4 hours earlier after 60 days, and so on. | |
It is found that the fixed stars take about 3 minutes 56 seconds less than the Sun to go round the Earth once. | It is found that the fixed stars take about 3 minutes 56 seconds less than the Sun to go round the Earth once. | ||
| − | '''1 Nakshatra Dina = 1 Savana Dina - 3 mins 56 secs = 23 Hrs 56 Mins 4 Secs''' | + | '''1 Nakshatra Dina = 60 Ghatikas''' |
| + | |||
| + | '''1 Nakshatra Day = 1 Savana Dina - 3 mins 56 secs = 23 Hrs 56 Mins 4 Secs''' | ||
==== Purpose of Nakshatra Dina ==== | ==== Purpose of Nakshatra Dina ==== | ||
| Line 97: | Line 138: | ||
1 Saura Dina (Solar Day) = Movement of Sun in the Rashi by 1 degree | 1 Saura Dina (Solar Day) = Movement of Sun in the Rashi by 1 degree | ||
| − | 1 Tithi (Lunar Day) = | + | 1 Tithi (Lunar Day) = Movement of Moon by 12 degrees |
1 Savana Dina (Civil Day) = 24 hours | 1 Savana Dina (Civil Day) = 24 hours | ||
Revision as of 22:20, 1 September 2020
| This article needs editing.
Add and improvise the content from reliable sources. |
Kalamana (Samskrit: कालमानम्) broadly refers to the measurement of time (Kala). Bharatiya shastrajnas have explained the various macrocosmic and microcosmic time systems and depending on the needs of particular topics in astronomy, different scales and units of time are used. On the macrocosmic scale, the Yuga system has been described, whereas on the microcosmic scale, a small unit of time Truti (1/33750 of a second) has been mentioned by Bhaskara II. We mention the macrocosmic time scales (Svetavaraha kalpa, Vaivasvata Manvantara etc) only in the samkalpa of our daily puja rituals.[1]
Introduction
On the day to day basis, however, we use the classic Panchanga (5 elements namely, Tithi, Vara, Nakshatra, Karana and Yoga) which measures time on a working scale, on a daily basis, to perform any activity of importance in our lives such as to determine Muhurta or auspicious times as well as to determine time for Shraddha and other Pitr karmas. The present article Kalamana discusses the aspects of Suryodaya, Suryastamaya or sunrise and sunset timings, Chandrodaya timings, Tithi, Nakshatra, Paksha (fortnight), Vara (day of the week), Samvatsara (year) and their determination. It may be noted that while some factors such as sunrise and sunset, moon-rise, rashis, sankramanas are common in all parts of India, some calculations such as of the day or a year are set variously by people of different cultures of India.
Many of these factors are based on simple natural observations, earth, moon and planetary motions and seasons - all of which are pratyaksha pramanas (visible evidence) in the nature around us manifesting the environmental changes. It is common knowledge that it is a day with sunrise, a night with sunset, high and low tides with lunar movements, rashis associated with the movement of moon in nakshatras, formation of new leaves and leaf shedding indicates seasonal change with Vishvat (equinoxes) so on and so forth.
It is only with deep respect for the intellect and keen observation of our ancient maharshis, rsis and later day ganita and jyotisha shastrajnas that we can appreciate the systematic work done by them - not requiring huge telescopes or light measuring instruments - to leave a legacy of astronomical wealth for us.
Here we discuss a few important astronomical concepts, briefly, that are in use in our present day calendars, without delving deep into the mathematical calculations used to arrive at them.
नवमानानि ॥ Nine Kinds of Time
Surya Siddhanta is one of the oldest texts and accepted by many scholars as an authentic source of information regarding the astronomical calculations and specifications. Manaadhyaya (14th Adhyaya) of Surya Siddhanta is referred here to understand the different kinds of Kala that we use in day to day lives.
ब्राह्मम् दिव्यम् तथा पित्र्यम् प्राजापत्यम् गुरोस् तथा । सौरम् च सावनम् चान्द्रम् आर्क्षम् मानानि वै नव ॥
चतुर्भिर्व्यवहारोऽत्र सौरचान्द्रार्क्षसावनैः।बार्हस्पत्येन षष्ट्यब्दा ज्ञेया नान्यैस्तु नित्यशः॥ (Sury. Sidd. 14.1-2)[2]
There are nine Manas or measurements of time (kinds of time). They are
- ब्राह्मम् ॥ Braahmam (Of Brahma)
- दिव्यम् ॥ Divyam (Of Devatas)
- पित्र्यम् ॥ Of Pitrs
- प्राजापत्यम् ॥ Of Prajapati
- गुरोः (बार्हस्पत्यम्) ॥ Of Guru (Brhaspati)
- सौरम् ॥ Of Surya
- सावनम् ॥ Of Savana
- चान्द्रम् ॥ Of Chandra
- आर्क्षम् (नाक्षत्रम्) ॥ Aarksham (Of Nakshatra)
The Manas, measures of time, which are used in daily activities are four in number - सौरचान्द्रार्क्षसावनैः । Solar, Lunar, Sidereal, and the Savana (Civil). The Mana of Jupiter (Barhaspatya) is used for determining the Shasthtyabda (60 Samvatsaras) or calculation of how a person attains 60 years of age. The remaining four Manas are not used for daily activities.[3]
While Suryasiddhanta is an astronomical text which is fundamentally a scientific treatise, Dharmashastra Nibandha texts such as Dharmasindhu and Nirnaya Sindhu also help us in determining the different Manas and lays down the vidhis associated with them. According to Dharmasindhu
तत्र कालः षड्विधः ॥ वत्सरः अयनम् ऋतुर्मासः पक्षो दिवस इति॥ (Dharm. Sind.1)[4]
Kala is of six kinds. Vatsara (वत्सरः) - one year, Ayanam (अयनम्) - half of a year or six months, Rtu (ऋतुः) - one season or two months, Masa (मासः) - one month or 30 days, Paksha (पक्षः) - one fortnight or 15 days, and Divasa (दिवसः) - one day.
It may be noted that the six kinds of time mentioned in Dharmasindhu are discussed in Suryasiddhanta also.
सौरमानम् ॥ Saura Mana
It is long known to our ancient seers that it is the earth that revolves around the sun in an ecliptic path. However, the time is calculated based on using the earth as a reference, and thus we say sun is revolving around the earth. We see in the sky that due to the diurnal motion, the Sun rises in the eastern horizon, moves up in the sky westward and sets in the western horizon. From the sunset to the next sunrise, it will be below the horizon during the night. It is common knowledge all over the world that this period of time between the sunrise and sunset is called a Day. However, our seers have calculated and defined a Day, not just with respect to the Earth but also with other cosmic references and specified the purpose where such a measure of time is to be used.
सौरदिनम् ॥ Saura Dina (Solar Day)
सौरेण द्युनिशोर्मानं षडशीतिमुखानि च। अयनं विषुवच्चैव सम्क्रान्तेः पुण्यकालता॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.3)[2]
With reference to Earth the Sun's motion along the ecliptic path, in the rashi, is about 1° per day. This is called a Solar Day.
षडशीतिमुखानि ॥ Shadasheeti Mukhas
There are four Shadasheeti Mukhas in a year.
तुलादि षडशीत्यह्नाम् षडशीतिमुखम् क्रमात् । तच्चतुष्टयम् एव स्याद् द्विस्वभावेषु राशिषु ॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.4)
Every eighty-sixth solar day reckoned from the time of Tula Sankramana (Day the Sun enters Tula rashi) is called Shadasheeti Mukha in succession. They are four in number and happen when Sun is in 4 Dvisvabhava Rashis, namely Dhanas (26°of Saggitarius), Meena (22° of Pisces), Mithuna (18° of Gemini) and Kanya (14° of Virgo) rashis.
पितृपक्षम् ॥ Pitrpaksha
ततः शेषाणि कन्याया यान्य् अहानि तु षोडश । क्रतुभिस् तानि तुल्यानि पितृऋणाम् दत्तम् अक्षयम् ॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.6)
After the 4th Shadasheethi Mukha (in Kanya), the remaining 16 solar days of the solar month when Sun is in Kanya rashi are equivalent to the time of Yajna, (kala when any good actions give great merit) and in these days dana offered to Pitrs will give infinite merit.[5]
From this we understand that, Shraddha for Pitrs should happen when Sun is in Kanya rashi starting from 15° to 30° according to Saura Mana. However, in the present times, Saura Mana is not used. According to Purnimanta system, Krishna paksha of Ashvini month (dark half of month of Ashvini) and according to Amanta system, Krishna paksha of Bhadrapada month (dark half of the month of Bhadrapada) i.e., calculated according to Chandra Mana are the days of Pitrpaksha followed by people.[3]
सङ्क्रान्तयः ॥ Sankrantis
The time at which Sun enters into an new rashi is termed Sankranti.
भचक्रनाभौ विषुवद्द्वितीयं समसूत्रगम् । अयनद्वितयं चैव चतस्रः प्रथितास्तु ताः॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.7)
In the middle of the nakshatra chakra (sphere of stars) the two equinoxes (Vishuvats in Mesha and Tula rashis) are diametrically opposed and so are the two solistices (Ayanas in Karkataka and Makara) in the ecliptic path.
The Shadasheeti Mukhas happen when Sun moves in the four rashis namely, Mithuna, Kanya, Dhanus, and Meena as described above (Surya. Siddhanta 14.4), the remaining four sankrantis (in Vrishabha, Simha, Vrschika and Kumbha) are called Vishnupadi.
उत्तरायणम् दक्षिणायनम् च॥ Uttarayana and Dakshinayana
तयोर्मकरसङ्क्रान्तेः षण्मासेषूत्तरायणम् । कर्क्यादेस्तु तथैव स्यात् षण्मासा दक्षिणायनम् ॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.9)
From the time Sun enters Makara rashi (Capricorn) the six months are termed Uttarayana (northern movement of the Sun); in the same manner from the time Sun enters Karkataka (Cancer), the six solar months are called Dakshinayana (southern movement of the Sun).[3]
Purpose of Saura Dina
- Determining the length of the day and night
- Shadashiiti Mukhas
- Determine Uttarayana and Dakshinayana (the northern and southern paths of the Sun)
- Equinoxes and Solistices (Vishuvats etc)
- Sankrantis (the time of entry of Sun into a new rashi)
सौरमासं सौरवर्षं च ॥ Solar Month and Year
द्विराशिनादृतवः षदुक्ताशिशिरादयः । मेषादयो द्वादशैते मासास्तैरेव वत्सरः ॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.10)
Six Seasons are formed covering the time when Sun moves in two signs in a cyclic manner; Shishira (very cold season) is said to occur for two months when Sun enters Makara rashi and rest of the Rtus occur successively for two months. Starting from the Mesha rashi, the movement of Sun along the 12 rashis (returning back to Mesha rashi) in 12 months constitutes a Solar Year. Dharmasindhu refers to the above explanation of the solar year as follows
मेषादिषु द्वादशराशिषु रविभुक्तेषु पञ्चषष्ट्यधिकशतत्रयदिनैः सौरवत्सरः संपद्यते ॥ (Dhar. Sind. 1)[4]
Therefore, a solar month is the time taken by the Sun to cover a rashi (30°) along the ecliptic path.[3][1]
The time taken by the Sun to complete a revolution (360°) around the Earth, as observed from the Earth, is defined as a Saura Varsha (Solar Year). To complete the 360° revolution the Sun takes about 365.25 Savana or Civil days.[1]
Sayana and Nirayana Solar Years
As mentioned above Solar years refer to Sun's revolution, as observed from the Earth. However, depending on the points of reference chosen, we have two different types of solar years
- Nirayana or Sidereal Solar Year
- Sayana or Tropical Solar Year
Nirayana (Sidereal) Saura varsha is the time taken by the Sun to complete a revolution, along the ecliptic path, with reference to a fixed star. Careful observations carried out over a long time enabled our ancient astronomers to determine the duration of a Nirayana Solar Year as 365.256364 days (365 Days, 6 Hours, 9 Minutes, 9.8 secs).
Sayana (Tropical) Saura varsha is the time taken by the Sun to complete a revolution, along the ecliptic path, with reference to the Vishuvat in Mesha (Vernal equinox). This time has been determined to be equal to 365.242190 (365 Days, 5 Hours, 48 Minutes and 46 secs). It is this Sayana Saura varsha that determines seasons.[1]
Summary
1 Saura Dina (Solar Day) = Movement of Sun in a Rashi by 1° in ecliptic path
1 Saura Masa (Solar Month) = Movement of the Sun across one Rashi (30°) in ecliptic path = 30.43803 days
1 Saura Varsha (Solar Year) = 365.25 Savana or Civil days
सावनमानम् ॥ Savana Mana
सावनदिनम्॥ Savana Dina (Civil Day)
उदयाद् उदयम् भानोः सावनम् तत् प्रकीर्त्यते । सावनानि स्युरेतानि यज्ञकालविधिस्तु तैः ॥
सूतकादिपरिच्छेदो दिनमासाब्दपास्तथा । मध्यमा ग्रहभुक्तिस्च सावनेन प्रकीर्त्यते ॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.18-19)[2]
The duration between two successive risings of the Sun is called a Savana Dina or Civil Day.[3]
Observations of sunrise over a very long time has revealed that the duration of a day is not constant but varies from day to day although very slightly. An average calculated based on the observations is referred to as the Mean Solar Day or Mean Civil day. Savana Dina is divided into 60 equal parts called Ghatikas or 24 equal parts called Hora (hours). Thus the 24 hour day that is used for our regular daily activities is the Savana Dina.[1]
1 Savana Day (Civil Day) = 60 Ghatikas = 24 Hours
Purpose of Savana Dina
- Savana days are used to determine the time of to perform yajnas.
- Determine Asoucha or Sutaka due to birth and death
- Limits of Chandraayana and other vratas
- Determine the rulers of the day, month and year
- To calculate the mean motion of planets.
चान्द्रमानम् ॥ Chandra Mana
तिथिः ॥ Tithi (Lunar Day)
अर्काद्विनिस्सृतः प्राचीं यद्यात्यहरहश्शशी। तच्चान्द्रमानम् अम्शैस्तु ज्ञेया द्वादशभिस्तिथिः॥
तिथिः करणम् उद्वाहः क्षौरम् सर्वक्रियास् तथा। व्रतोपवासयात्राणाम् क्रिया चान्द्रेण गृह्यते॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.12-13)[2]
The time in which the Moon being separate from the Sun (after a conjunction) moves daily to the east is the measurement for the moon (चान्द्रमानम्) Chandra Mana. The time taken by the Moon to cover exactly a distance of 12° relative to the Sun, is defined as Tithi or Lunar Day.[3]
The Moon, like the Sun, moves from west to east with reference to the fixed stars. Since the moon moves faster than the sun, starting from a new moon, the moon gains about 12° per day over the Sun, i.e., one Tithi per day, thus the chandra masa has 30 tithis. The half-lunar month from a new moon to the succeeding full moon is called Shukla Paksha (the bright fortnight) and the other half-lunar month from the full moon to next new moon is called Krshna Paksha (dark fortnight). The lunar month is a natural unit for a month. It is important to note that the beginning and end of a lunar month are naturally marked by two successive new moons.[1]
Sidereal Period of Moon
The moon moves along its own orbit, with a slight inclination towards the ecliptic path. It is found that the moon takes an average period of 27.32166 days to complete a revolution with reference to the fixed stars. This time interval is called the Sidereal Period of Moon, since the moon takes this much time to complete an angular revolution of 360°, its motion per day is given as 360/27.32166 = 13°10'. In comparison to this, the sun's motion along the ecliptic, in the same direction, is about 1° per day. Thus the moon overtakes the Sun by about 12°10' per day.[1]
चन्द्रमासं चन्द्रवर्षं च ॥ Lunar Month and Year
If the Sun and Moon are moving in the same direction, in which case their celestial longitude is the same, as seen from the Earth, the moon is said to be "new" or it is called Amavasya or New Moon Day. After 24 hours the moon would have moved ahead of the Sun by about 12°10'. This increasing separation of the moon from the sun goes on at the rate of 12°10' per day until it reaches 360°. At this point the moon will be in conjunction (or in the same direction) as the sun, resulting in a new moon. The interval between two successive new moons is called the synodic period of the Moon ("synodic" means successive conjunctions of the same bodies). This synodic period of the Moon is defined as a Lunar month (Chandra Masa). Thus one lunar month = 29.530589 days (29 Days, 12 Hours, 44 Minutes, and 2.9 secs).[1]
Dharmasindhu elaborates about the course of a lunar month, when the Moon goes through a cycle of phases, from new moon to full moon and then to new moon again.
शुक्लप्रतिपदादिदर्शांन्तैश्चैत्रादिसंज्ञैर्द्वादशभिर्मासैश्चतुःपञ्चाशदधिकशतत्रयदिनैः सति मलमासे त्रयोदशभिर्मासैश्चान्द्रो वत्सरः॥ (Dhar. Sind. 1)[4]
From the Shukla Pratipat tithi till the end of Amavasya, there are 30 tithis; together they constitute one Chandra-masa or Lunar month namely Chaitra, etc. 12 such Lunar months make up a Lunar Year having 354 days (savana days). When an Adhika masa is present there are 13 months a lunar year.
Purpose of Chandra Mana
- Determination of Tithi, Karana (half of Tithi)
- Determine the auspicious time for samskaras like marriage
- Determine the appropriate time for activities such as shaving, tonsure
- To determine the time for Vratas, Upavasas, Yatras
1 Tithi (Lunar Day) = Time taken by the Moon to cover a distance of 12° relative to the Sun
1 Chandra Masa (Lunar Month) = 29.530589 days
नाक्षत्रमानम् ॥ Nakshatra Mana
नाक्षत्रदिनम् ॥ Nakshatra Dina (Sidereal Day)
नाडी षष्ट्या तु नाक्षत्रमहोरात्रं प्रकीर्तितम् । तत्त्रिम्शता भवेन्मासः सावनोऽर्कोदयैःस्मृतः॥ (Sury. Siddh. 1.12)
The time which contains sixty ghatikas is called a Nakshatra Ahoratra (a sidereal day and night) or Day and a Nakshatra masa (a sidereal month) consists of thirty Nakshatra Ahoratras.
भचक्रभ्रमणम् नित्यम् नाक्षत्रम् दिनम् उच्यते। नक्षत्रनाम्ना मासास् तु ज्ञेयाः पर्वान्तयोगतः ॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.15)[2]
The time taken for one revolution of the sphere of stars is called a sidereal day. The time taken by the fixed stars to go around the earth is called a Nakshatra Dina or Sidereal Day; and this time is equal to the period of the rotation of the Earth.
Sidereal is a term used to refer to stars. It is important to note that the time taken by the fixed stars to go round the Earth once is not the same as that taken by the Sun. While all the celestial bodies appear to move from the east to west due to the diurnal motion, the Sun would have moved from west to east along the ecliptic by about 1°, relative to the stars. Therefore, the fixed stars take a little less than 24 hours (mean civil day) to complete a rotation around the Earth. As a natural consequence if a particular star rises in the eastern horizon at a particular time today, it will rise about two hours earlier after 30 days, 4 hours earlier after 60 days, and so on.
It is found that the fixed stars take about 3 minutes 56 seconds less than the Sun to go round the Earth once.
1 Nakshatra Dina = 60 Ghatikas
1 Nakshatra Day = 1 Savana Dina - 3 mins 56 secs = 23 Hrs 56 Mins 4 Secs
Purpose of Nakshatra Dina
- Naming of lunar months is from the Nakshatras; the name of a lunar month is determined from the nakshatra in which moon is present at the time of Purnima (15th day of full moon) tithi (with a few exceptions).
Summary
1 Saura Dina (Solar Day) = Movement of Sun in the Rashi by 1 degree
1 Tithi (Lunar Day) = Movement of Moon by 12 degrees
1 Savana Dina (Civil Day) = 24 hours
1 Nakshatra Dina (Sidereal Day) = 23 Hrs 56 Mins 4 Secs
Four Other Manas
पितृमानम् ॥ Pitr Mana
त्रिम्शता तिथिभिर्मासश्चान्द्रः पित्र्यमहः स्मृतम्। निशा च मासपक्षान्ते तयोर्मध्ये विभागतः॥ (Sury. Siddh. 14.14)[2]
Thirty tithis make a lunar month (mentioned under Tithis) which constitutes one day and night for the Pitrs. The end of Chandramasa (lunar month) i.e., the end of the New moon day (Amavasya) corresponds to the noon time for the Pitrs and the end of the Full moon day (Purnima) corresponds to the midnight time for the Pitrs. Thus the middle of Shukla Ashtami tithi corresponds to the start of the day for Pitrs and the middle of Krshna Ashtami tithi corresponds to the start of the night for the Pitrs.[1] The Bhugola Adhyaya of Surya Siddhanta further discusses this topic establishing Amavasya as the noon time and Purnima as midnight for Pitrloka (Page 767-768 of Reference[3]).
Purpose of Pitr Mana
- Determine the Masikas (performing monthly Pitr kriyas upto one year of death).
- Determine the time of annual Shraddha
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Rao, S. Balachandra. (2000) Indian Astronomy, An Introduction. Hyderabad: Universities Press (India) Limited. (Page 39-50)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Surya Siddhanta (Adhyaya 14)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Pt Mahavir Prasad Srivastav (1940 First Edition) Surya Siddhanta with Vijnana Bhashya, Parts 1 and 2. Allahabad: Dr. Ratnakumari Svadhyaya Sansthan. (Page 794 -)
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 The Dharmasindhu by Kasinath Upadhyaya (1986 Reprint Edition) Delhi: Sri Satguru Publications (Pages 1-7)
- ↑ Pt. Bapu Deva Sastri (1861) Translation of the Surya Siddhanta and Revision of Siddhanta Siromani Translated by Lancelot Wilkinson. Calcutta: Asiatic Society. (Pages 91-)