Bharatiya Samskrtika Parampara (भारतीयसांस्कृतिकपरम्परा)
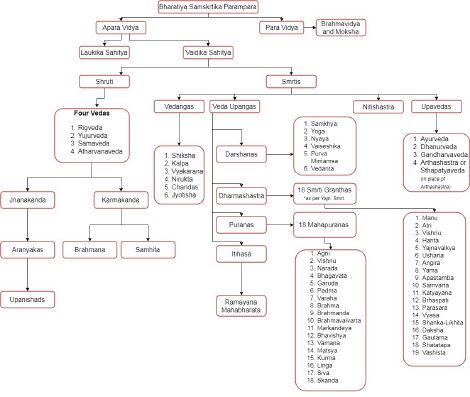
Bharatiya Samskrtika Parampara (Samskrit : भारतीयसांस्कृतिकपरम्परा) or Indian Traditional Literary series of works include all major components of Bharatiya texts coming from a vast repository of Samskrit literature preserved through oral tradition as well as those in the form of manuscripts and other written formats. Samskrit literature can be classified under two headings viz., Vedas and Vaidika Sahitya consisting of ancient literature and Laukika Sahitya including the more recent classical samskrit works. The Vedas and Vaidika Sahitya is a collection of the authoritative texts of Sanatana Dharma, while Laukika Sahitya embodies the later developments in classical Sanskrit literature.[1]
Vedas and Vaidika Sahitya
A whole body of texts are included under this heading:[1][2][3]
- Shrutis also called Amnaya (आम्नाय) and Trayi (त्रयी) (Include Vedas, Vedabhashyas, Brahmanas, Aranyakas, Upanishads example : Rigveda, Yajus samhita, Brhdaranyaka, Chandogya Upanishad)
- Smritis (Vaidika Vangmaya such as Vedangas, Smritis or Dharmashastras, Puranas, Itihasa)
- Agamas (Example : Shaiva and Vaishnava Agamas)
- Darsanas (Astika Darshanas, example : Nyaya darshana)[1]
Although the word Smrti is used in general to denote the non-Shruti literature, it is often used to refer to the Dharmashastras, which describe the code of conduct for everyone.[1] In the scope of the present project, word Smrti is used to represent the whole of the non-Shruti literature as well as specifically refer to Dharmashastras (Smrti granthas like Manusmrti, Yajnavalkya smrti).
Laukika Sahitya
The classical literary writings include different types of writings classified variously :[1]
- Mahakavyas (Poetry, example : Kalidasa Mahakavi's Raghuvamsha)
- Rupakas or Natakas (Drama, example : Mricchakatika, Pratimanataka)
- Alankara shastragranthas (Example : Kavyaprakasha, Dhvanyaloka)
- Gadya kavyas (Prose, example : Kadambari)
- Charitraka kavyas (Historical presentations, example : Rajatarangini)
- Champu kavyas (Mix of prose and poetry, example : Champu Ramayana)
- Katha kavyas (Stories, example : Brhatkatha, Kathasaritsagara)
- Nitikavyas (Didactic poetry, example : Panchatantra and Hitopadesha)
In DharmaWiki, articles pertaining to the Vedas and Vaidika Vangmaya are discussed while information pertaining to Laukika Sahitya is beyond the scope of this project (except for a few references). A flowchart of the classification of Vaidika and Laukika Sahitya has been attempted with the sources of the material as given in the article.
The Shrutis
The Vaidika texts were memorized and transmitted orally, from one generation to next, hence preserved over thousands of years. There are two classifications of Hindu texts: Shruti – that which is heard, and Smriti – that which is remembered. The supremacy of Vedas has been emphasized in Manusmrti as follows
बिभर्ति सर्वभूतानि वेदशास्त्रं सनातनम् । तस्मादेतत्परं मन्ये यज्जन्तोरस्य साधनम् । । १२.९९ (Manu. Smrt. 12.99)[4]
bibharti sarvabhūtāni vedaśāstraṃ sanātanam । tasmādetatparaṃ manye yajjantorasya sādhanam । । 12.99 । ।
Meaning: The eternal Veda shastra upholds or protects all beings (by being their flawless guideline). Those endeavoring for the welfare of all beings, regard Vedas as their supreme authoritative instrument in achieving it.
The Vedas (Samhita, Brahmana, Aranyaka and Upanishads) called Shrutis, are passed on to generations of students and are memorized by hearing the mantras from the guru (guru-shishya parampara). Rishis have received the Vedas through revelation and hence Vedas are considered to be apauruṣeya, or entirely superhuman, without any author. The Vedas are the foundational authority for the people who follow Sanatana Dharma.[5][6]
The Four Vedas are:
Veda Vargeekarana or classification of the Vedas is extensive, for example Rig veda is divided in Astaka and Mandala Kramas. The Yajur Veda is divided into two parts - The Shukla and the Krishna. The Krishna or the Taittirya shaka is the older book and the Sukla or the Vajasaneya is a later revelation to sage Yajnavalkya from Surya. The Rig-Veda is divided into twenty one shakas, the Yajur Veda into one hundred and nine shakas, the Sama Veda into one thousand shakas and the Atharva Veda into fifty shakas. In all, the Veda is thus divided into one thousand one hundred and eighty shakas or recensions.[5]
Each Veda has been sub-classified in textual content again into four major text types[5]:
- The Samhitas that comprise of mantras and benedictions.
- The Brahmanas that contain explanation of Mantras and rituals
- The Aranyakas that are mystical texts which give philosophical interpretation of the rituals. These are intended for the Vanaprasthas or hermits, who prepare themselves for taking Sanyasa
- The Upanishads that discuss meditation, philosophy and spiritual knowledge.
The subject matter of the whole Veda is divided into Karma-Kanda (कर्म खण्ड), Upasana-Kanda (उपासना खण्ड) and Jnana-Kanda (ज्ञान खण्ड). The Karma-Kanda or ritualistic section deals with various yajnas and associated kriyas. The Upasana-Kanda or worship-section deals with various kinds of worship or meditation. The Jnana-Kanda or knowledge-section deals with the knowledge of Brahman. The Samhitas and the Brahmanas constitute Karma-Kanda; the Aranyakas Upasana-Kanda; and the Upanishads Jnana-Kanda.[1][5]
Main Components of Shrutis
The Samhitas
Samhitas are primarily a collection of the mantras, Riks in Rigveda, Yajus of Yajurveda, Samans of the Samaveda and those of Atharvaveda. The Rig-Veda Samhita is the oldest sacred literary text of the Hindus. The Yajur-Veda Samhita is mostly in prose and explaining the procedures of the yajnas and yagas, supplementing the Rig-Vedic Mantras. The Sama-Veda Samhita, shortest of all vedas, is mostly borrowed from Rig-Vedic Samhita sung with melody especially during the Soma yajnas. the Atharva-Veda Samhita is meant to correct the mispronunciations and wrong performances that may accidentally be committed during the yajnas. Atharvaveda contains mantras on many subjects such as socio-political aspects, medicine, agriculture etc along with philosophical thoughts.[1][7]
The Brahmanas
Brahmanas are injunctions or vidhis for the performance of shrauta yajnas.[6] Important with respect to the procedural aspects of Vaidika yajnas they explain the meaning and gudartha (hidden meanings) of the Samhita parts. They are that portion of the Vedas which apart from stating the vidhis, explain their origin and detailed explanation with illustrations in the form of legends and anecdotes, thus appear distinct from the "mantra" portions of the Samhitas.[8]
While not many variations in the names and number of Brahmanas are seen for Rigveda, Yajurveda and Atharvaveda, however, Samaveda associated with the highest number of Brahmanas, is opined to have some differences in number and names of Brahmanas, by scholars.
According to Swami Sivananda, six brahmanas : the Tandya or Panchavimsa, the Shadvimsa, the Chhandogya, the Adbhuta, the Arsheya and the Upanishad Brahmanas belong to the Sama Veda.[5]
According to Dr. Gopal Reddy in Sanskruta Sahitya Charitra nine Brahmanas are mentioned Tandya, Shadvimsha, Samavidhana, Arsheya, Devataradhya, Upanishad, Samhitopanishad, Vamsha, and Jaiminiya Brahmanas.[1]
According to Shri. Shriram Adhikari (Vedic Heritage Portal), eight Brahmanas for Samaveda are available as given in the above list except that he lists Chandogya-Upanishad brahmana and instead of Upanishad brahmana and Jaiminiya brahmana is missing.[9] Dr Shashi Tiwari lists two Brahmanas in addition to the 9 listed by Dr. Gopal Reddy, as JaiminiyaArsheya Brahmana and Jaiminiyopanishad Brahmana making it a total of 11 Brahmanas available for Samaveda.[10]
The Aranyakas
Each of the Vedas are associated with an Aranyaka except Atharvaveda. Usually Aranyakas are present as the concluding part of the Brahmanas, however, due to the non-availability of Aranyakas for Atharvaveda, Upanishads stand as independent works in this veda. Aranyakas and Upanishads are like the parishistas (appendices) to the Brahmanas.
Aranyakas are said to be those texts to be studied by people in their vanaprastha ashrama, living a life of seclusion in the forests. Subject material of Aranyakas consists of the partly modified versions of yajnas and vratas apart from the spiritual matters. These tattvas and theosophical matters are extensively elaborated in the Upanishads. Karma and Jnana margas appear to be balanced in the Aranyakas. Upasana (meditation), Brahmavidya along with the Pranavidya (Knowledge of Breath), details of origin of sristi, meditation on Pranava are described elaborately so that the residents of the forest can practice them in the quiet solitude of the forests. The number of Aranyakas was once said to be 130, but now many are lost.[1][11]
The different brahmanas and Aranyakas associated with different veda shakas are listed in the table below.[1][5][12]
| RigVeda | Yajurveda | Samaveda | Adharvaveda | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Krishna | Shukla | |||
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
None available |
The Upanishads
The Upanishads are the concluding portions of the Aranyakas, and thus last portions of the Vedas, the mukhya upanishads being essentially difficult to be separated from their Aranyakas. The teaching based on them is called Vedanta. For example, Aiteraya Upanishad is the parishista of Aiteraya Brahmana of Rigveda.[1][8]
Etymologically the name Upanishad has been variously interpreted. The form of teaching was that of the dialogues transmitted orally, hence they are also included in Shrutis. Significant feature is that no authorship has been recorded and Upanishads are regarded as revelations to seers. Upanishads have been regarded as one among the Prasthana Trayam, the other two included are Brahmasutras and Bhavagad Gita.
The concepts of Brahman (Ultimate Reality) and Ātman (Soul, Self) are central ideas in all the Upanishads, and "Know your Ātman" their thematic focus.[13] The Upanishads are the very foundation of the siddhantas and tattvas of Sanatana Dharma applicable to man in every walk of life philosophical thought and its diverse traditions. Of all the texts included in Vaidika Vangmaya, Upanishads have been widely studied by many people of the world, and in the present day the theosophical ideas and vidyas that have been discussed in the Upanishads have made a great impression on mankind. Thus Upanishads throw light on Brahmavidya, aid in destroying the Avidya of Mumukshus (persons interested in attaining Moksha) causing attainment of Moksha or Brahmaloka by removing the three kinds of Dukha (pain).[1]
There are as many Upanishads to each Veda as there are Sakhas, branches or recensions, i.e., 21, 109, 1000 and 50 respectively to the four Vedas, the Rig-Veda the Yajur Veda, the Sama Veda and the Atharva-Veda.[5]
More than 200 Upanishads are known, of which the first dozen or so are the oldest and most important and are referred to as the principal or main (mukhya) Upanishads from the Vedantic point of view. The mukhya Upanishads are found mostly in the concluding part of the Brahmanas and Aranyakas and were, for centuries, memorized by each generation and passed down verbally. Muktikopanishad and Narayanopanishad lists 108 Upanishads and of them Dasa-Upanishads are
ईश-केन-कठ-प्रश्न-मुण्ड-माण्डूक्य-तित्तिरः । एेतरेयं च छान्दोग्यं बृहदारण्यकं तथा ॥
īśa-kēna-kaṭha-praśna-muṇḍa-māṇḍūkya-tittiraḥ । ēētarēyaṁ ca chāndōgyaṁ br̥hadāraṇyakaṁ tathā ॥
Besides these Shvetashvatara, Kaushitaki and Maitrayaniya Upanishads are also listed as older ones. Shri Adi Shankaracharya has given bhashyam (commentary) for these ten principal Upanishads and has mentioned about Kaushitaki and Shvetasvatara Upanishads in his writings, though he did not write the bhasyam for these two Upanishads. These 13 Upanishads are based on the ancient vedic sources and advocate the tattava of Vedanta. The many other Upanishads that are currently available have arisen based on the particular sampradayas, thus we find mainly Shaiva, Vaishnava, Yoga and Shakteya Upanishads. The older Upanishads describe the places starting from Kuru, Panchala upto Videha indicating their place of origin. It is to be noted that in place of the many Vaidika devatas we find mention more of Brahman or Parabrahman (nirakara), showing the unity of divinity. Ancient (prachina) Upanishads mention Prkruti, Purusha and Brahma while the more recent (arvachina) Upanishads mention the deities Vishnu or Shiva and so forth.[1]
The Smrtis
The word Smrti is used in two senses. In a broad sense, is applied to all ancient non-Vedic works such as Panini's grammar, to the Shrauta, Grhya and dharma sutras, to Mahabharata, to Manu, Yajnavalkya and others. In a narrow sense, smrti and dharmashastras are synonyms as quoted by Manu (2.10). The word Smrti, however, occurs in Taittriya Aranyaka (1.2).[14] with respect to Dharma, is also referred by Gautama (Dharmasutras 1.2) and Vasishta (Dharmasutras 1.4) who cite Smrtis as the sources of dharma.[15]
Smrti literature includes that 'which is remembered', covering all the texts other than the Vedas.[5][2] According to Dr. Gopal Reddy they broadly include the following[1]
- Shad Vedangas (Shiksha, Vyakarana, Nirukta, Chandas, Kalpa, Jyotisha)
- Veda-Upangas (Puranas, Itihasa, Dharmashastras or Smrti granthas, Mimamsa and Nyaya shastras). Some scholars consider all the Shad Darshanas as Veda Upangas.[16]
- Upavedas (Ayurveda, Dhanurveda, Gandharvaveda, Arthashastra)
- Nitishastra (Dandaniti shastra)
A clear cut definition is not given as what all constitute the Smrti texts. There is a difference in the way the texts are classified by different scholars. Pratisakhyas, Anukramanikas and the more recent Nibandhas are also included under this broad category of Smrtis.
The Shad Vedangas
Vedangas are six topics, the study of which are required for the complete understanding of the Vedas. Each of these subjects are given by different seers, developed for the understanding of a student. The Six Angas are as follows :
- Shiksha is a knowledge of phonetics. Shiksha deals with pronunciation and accent. The text of the Vedas are arranged in various forms or Pathas (पाठ-s). The Padapatha (पदपाठः) gives each word its separate form. The Kramapatha (क्रमपाठः) connects the word in pairs.[5] Pratisakhyas are the angas of Shiksha granthas.
- Chandas is the knowledge of meters. This auxiliary discipline lays its focus on the metrical construction of vedic mantras and poetic meters, including those based on the number of syllables per mantra and those based on the duration of pronunciation of syllables in a mantra.
- Vyakarana is the knowledge of construction of words or grammar. This auxiliary discipline has focused on the rules of grammar and siddhiprakriya (सिद्धिप्रक्रिया | the process of deriving a word), so as to establish the exact form of words and sentences to properly express ideas.
- Nirukta gives the vyutpatti-artha (व्युत्पत्ति-अर्थ | etymology), explaining words, particularly those which are archaic and have a different ancient vedic usage with uncommon meaning. This auxiliary discipline has focused on developing a Nighantu which is a dictionary that has a collection of vedic usages. These words are analysed to establish the proper meaning of the words according to the context used in vedas.
- Jyotish deals with astronomy and astrology. It deals with the movements of the heavenly bodies, planets, etc., and their influence in human affairs.[5] This auxiliary Vedic discipline focused on time keeping.
- Kalpas are the texts that deal with the methods of yajna and other rituals composed in Sutra format. This field focused on standardizing procedures for Vedic Shrauta rituals, Smarta rituals associated with samskaras - major life events such as birth, wedding and death in family, as well as discussing dharmas laid down for the personal conduct and proper duties of an individual in different stages of his life.Sutras under this category include :
- Shrauta Sutras describe the procedures of Shrauta yajnas as per the veda shaka. Example : Haviryajnas, Somayajnas
- Grhya Sutras describe the procedures of Grhya yajnas pertaining to veda shakas. Example : Pakayajnas, Panchamahayajnas
- Dharma Sutras describe the rules pertaining to the Varna-Ashrama Dharmas (Smarta Karmas). Example : Baudhayana Dharmasutras, Apastamba Dharmasutras
- Sulba Sutras describe the mathematical and geometrical aspects of the construction of the vedic altars. Example : Baudhayana and Apastamba Sulbasutras[6]
The Upa-Vedas
According to Vishnupurana there are four Upa-Vedas or subsidiary Vedas, viz., the Ayurveda, the Dhanurveda, the Gandharva Veda and the Artha Shastra forming auxiliaries to the four Vedas[17]. Some scholars consider Sthapatya Veda as the fourth Upaveda instead of Arthashastra[5][3]. Sthapatya Veda or Shilpa Veda deals with the science of architectural engineering.
The Upavedas supplement the Vedas with more specific applications of Vedic teachings into the cultural field.
| S. No. | Upaveda Name | Concerned with | Associated with Veda |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | आयुर्वेदः || Ayurveda | Science of Health and Life | Rig Veda |
| 2 | धनुर्वेदः || Dhanurveda | Science of Warfare / Martial Arts | Yajurveda |
| 3 | गान्धर्ववेदः || Gandharvaveda | Music, poetry and dance | Sama Veda |
| 4 | अर्थशास्त्रम् || Arthashastra | Public administration, governance, economy and polity | Atharvaveda |
The Dharmashastras or Smrti Granthas
In a more specific sense Smrtis are ancient law-codes dealing with the sanatana Varnashrama Dharmas given by seers. They supplement and explain the ritualistic injunctions called Vidhis in the Vedas. The Smriti Shastra is based on the Sruti and stands next in authority to the Sruti. It explains and develops Dharma. Manusmrti explains that Shrutis comprise the Vedas, while Smrtis include the Dharmashastras.[15]
श्रुतिस्तु वेदो विज्ञेयो धर्मशास्त्रं तु वै स्मृतिः । śrutistu vedo vijñeyo dharmaśāstraṁ tu vai smr̥tiḥ । (Manu. Smrt. 2.10)[18]
It lays down the laws which regulate (Hindu) national, social, family and individual obligations. The laws for regulating society from time to time are codified in the Smritis. The Smritis have laid down definite rules and laws to guide the individuals and communities in their daily conduct and to regulate their manners and customs. They contain detailed instructions, according to the conditions of the time, to all classes of men regarding their duties in life. The Hindu learns how one has to spend his whole life from these Smritis. The duties of people in different Varnashramas and all ceremonies are clearly given in these books[5][19]. The Smritis prescribe certain acts and prohibit some others for a Hindu, according to one's birth and stage of life. The object of the Smritis is to purify the heart of a person and take him/her gradually to the supreme abode of immortality and make him/her perfect and free. These Smritis have varied from time to time. The injunctions and prohibitions of the Smritis are related to the particular social surroundings. As these surroundings and essential conditions of the Hindu society changed from time to time, new Smritis had to be compiled by the seers of different ages and different parts of India.[5]
वर्णादिधर्मस्मरणं यत्र वेदाविरोधकम् । कीर्तनं चार्थशास्त्राणां स्मृतिः सा च प्रकीर्तिता । (Shuk. Niti. 4.3.54)
varṇādidharmasmaraṇaṁ yatra vedāvirodhakam । kīrtanaṁ cārthaśāstrāṇāṁ smr̥tiḥ sā ca prakīrtitā । (Shuk. Niti. 4.3.54)
आर्षं धर्मोपदेशं च वेदशास्त्राविरोधिना । यस्तर्केणानुसंधत्ते स धर्मं वेद नेतरः || १२.१०६ || (Manu. Smrt. 12.106)[4]
ārṣaṁ dharmopadeśaṁ ca vedaśāstrāvirodhinā । yastarkeṇānusaṁdhatte sa dharmaṁ veda netaraḥ || 12.106 || (Manu. Smrt. 12.106)
Dharmasutras Vs Dharmashastras
Smrtis, the codified law books, otherwise known as Dharmashastras, are different texts as against the Dharmasutra works (Shrauta Sutras and Dharma Sutras) given in the Kalpas. Smrti texts have laid emphasis on the karmaushtana on the social front as compared to karmanushtana of an individual. These granthas contain information on the aspects of administration and governance, it may be said that as the number of kingdoms grew, so also the number of Smrti granthas.
Dharmasutras are the basis of Dharmashastra granthas. Dharmasutra granthas are cryptic, abbreviated with short explanations of the sutras, hence they required bhashyas or commentaries and tikas for understanding them.
Another point of debate among the scholars is whether the book named Manava-dharmashastra (मनव-धर्मशास्त्रम्) and Manusmrti are one and the same. Both these texts have been authored by Manu, who is considered as the Adipurusha (first in the human race), as per Samhita and Brahmanas. However, the aspects found in Manava-dharmashastra, which are found in other ancient texts, are not to be seen in Manusmrti. Hence is believed by scholars that Manava-dharmashastra and Manusmrti are two different texts and that Manusmrti is founded on the principles given in Manava-dharmashastra.[1]
Kanchi Sri Chandrasekharendra Saraswati Paramacharya, explains that some Smrtis do not contain instructions with regard to all observances. The matters explained in one Smrti may not be found in an other, thus giving rise to doubts in acharas which are to be cleared by using the works called "Dharmashastra Nibandhanas". These nibandhanas do not leave out any rite or dharma. Nirnayasindhu (by Kamalakara Bhatta), Vaidyanatha Dikshitiyam, Dharmasindhu are accepted and referred to authoritative texts in the present day.[20]
Number of Smritis
Of such law-givers Manu, Yajnavalkya and Parasara are the most celebrated. Hindu society is founded on, and governed by the laws made by these three great seers. Of the Manu Smriti, Yajnavalkya Smriti and Parasara Smriti, Manu is the oldest law-giver. The Yajnavalkya Smriti follows the same general lines as the Manu Smriti and is next in importance to it. Manu Smriti and Yajnavalkya Smriti are universally accepted at the present time as authoritative works all over India. Yajnavalkya Smriti is chiefly consulted in all matters of Hindu Law and finds application in the Judicial System of the Government of India.
In ancient times the number of Smrtis must have been small.
- Gautama mentions only Manu, although he speaks of dharmashastras (9.19).
- Vashishta names 5 smrtikaras - Gautama, Prajapati, Manu, Yama and Harita.
- Manu speaks of six authors besides himself namely - Atri, son of Utathya, Bhrugu, Vashishta, Vaikhanasa and Saunaka.
- Baudhayana names seven besides himself, as the authors of dharma.
- Apastamba mentions 10 smritikaras, some of whom are mere names their works are not available.
There are eighteen main Smritis or Dharma Shastras, accepted by many scholars, howevever, as seen in the case of many other texts there are different versions of Smrti granthas. Yajnavalkya Smrti is probably one of the earliest Smrti which enumerated twenty expounders of dharma (including himself and counting Shanka and Likhita as two distinct persons) as seen in the following list[15]
मन्वत्रिविष्णुहारीत याज्ञवल्क्योशनोऽङ्गिराः । यमापस्तम्बसंवर्ताः कात्यायनबृहस्पती । । १.४ । । (Yajn. Smrt. 1.4)[21]
manvatriviṣṇuhārīta yājñavalkyośano'ṅgirāḥ । yamāpastambasaṁvartāḥ kātyāyanabr̥haspatī । । 1.4 । ।
पराशरव्यासशङ्ख लिखिता दक्षगौतमौ । शातातपो वसिष्ठश्च धर्मशास्त्रप्रयोजकाः । । १.५ । । (Yajn. Smrt. 1.5)
parāśaravyāsaśaṅkha likhitā dakṣagautamau । śātātapo vasiṣṭhaśca dharmaśāstraprayojakāḥ । । 1.5 । ।
- Manu Smrti
- Atri Smrti
- Vishnu Smrti
- Harita Smrti
- Yajnavalkya Smrti
- Ushanas Smrti
- Angira Smrti
- Yama Smrti
- Apastamba Smrti
- Samvarta Smrti
- Katyayana Smrti
- Brhaspati Smrti
- Parashara Smrti
- Vyasa Smrti
- Shanka-Likhita Smrti
- Daksha Smrti
- Gautama Smrti
- Shatatapa Smrti
- Vasishta Smrti
According to Sri. Chandrasekharendra Mahaswamiji, [20] there are 18 Smrtis given by - Manu, Parasara, Yajnavalkya, Gautama, Harita, Yama, Visnu, Sankha, Likhita, Brhaspati, Daksa, Angiras, Pracetas, Samvarta, Acanas, Atri, Apastamba and Satatapa are the eighteen sages who mastered the Vedas with their superhuman power and derived the Smrtis from them.
According to Dr. Gopal Reddy[1], the eighteen Smrtikartas are Manu, Yajnavalkya, Atri, Vishnu, Harita, Ushanas, Angira, Yama, Katyayana, Brhaspati, Parasara, Vyasa, Daksha, Gautama, Vasishta, Narada, Bhrgu, and Angirasa.
According to Swami Sivananda[5], the eighteen Smrtis are those of Manu, Yajnavalkya, Parasara, Vishnu, Daksha, Samvarta, Vyasa, Harita, Satatapa, Vasishtha, Yama, Apastamba, Gautama, Devala, Sankha-Likhita, Usana, Atri and Saunaka.
The laws of Manu are intended for the Satya Yuga, those of Yajnavalkya are for the Treta Yuga; those of Sankha and Likhita are for the Dvapara Yuga; and those of Parasara are for the Kali Yuga. The laws and rules which are based entirely upon our social positions, time and clime, must change with the changes in society and changing conditions of time and clime. Then only the progress of the Hindu society can be ensured.[5]
The Nitishastra (Dandaniti)
In Mahabharata's Shantiparva we find the mention of Dandaniti shastra given to the world by Brahma, which is a text said to comprise of 100,000 adhyayas expounding the purusharthas and achieving them.
दण्डनीत्यां प्रणीतायां सर्वे सिद्ध्यन्त्युपक्रमाः। कौन्तेय सर्वभूतानां तत्र मे नास्ति संशयः॥ 1 (Maha. Shan. Parv. 12.15.29)
daṇḍanītyāṁ praṇītāyāṁ sarve siddhyantyupakramāḥ। kaunteya sarvabhūtānāṁ tatra me nāsti saṁśayaḥ॥ (Maha. Shan. Parv. 12.15.29)
दण्डश्चेन्न भवेल्लोके विनश्येयुरिमाः प्रजाः। जले मत्स्यानिवाभक्ष्यन्दुर्बलान्बलवत्तराः॥ (Maha. Shan. Parv. 12.15.30)
daṇḍaścenna bhavelloke vinaśyeyurimāḥ prajāḥ। jale matsyānivābhakṣyandurbalānbalavattarāḥ॥ (Maha. Shan. Parv. 12.15.30)
चातुर्वर्ण्यप्रमोदाय सुनीतिनयनाय च। दण्डो विधात्रा विहितो धर्मार्थौ भुवि रक्षितुम्॥ (Maha. Shan. Parv. 12.15.35)
cāturvarṇyapramodāya sunītinayanāya ca। daṇḍo vidhātrā vihito dharmārthau bhuvi rakṣitum॥ (Maha. Shan. Parv. 12.15.35)
Summary: In Vaisampayana's instruction of rajaniti to Arjuna, he stresses that with the appropriate application of Dandaniti (दण्डनीतिः) all the beings of all worlds will be alert to conduct themselves appropriately. If not so, all the creatures will perish and just like the big fish eats the small fish, a stronger person will harm a weaker person. Brahma created this system for the happiness of the people of the four varnas and that everyone follows niti for the protection of both dharma and artha (money).[22]
Later on, Shiva, condensed them into a text called "Vaisalaksha (वैशालाक्ष)" with 10,000 adhyayas. Indra further condensed this shastra to a comprehensive text called "Bahudantakashastra (बाहुदन्तक-शास्त्रम्). Sukracharya further condensed it to a 1000 adhyayas and named the text as "Aushanasaniti (औशनसनीतिः) or Shukraniti (शुक्रनीतिः). This story in Mahabharata indicates that the base text is the same Dandanitishastra grantha, which underwent changes over a time period. Dandaniti shastra describes Arthashastra, Rajaniti, Social aspects, Shilpashastra, and even Rasayana shastra.[1]
The Puranas
The Puranas as a class of literature existed from very ancient times. For example, Taittriya Aranyaka (2.10) speaks of 'Brahmanas, Itihasas, Puranas and Narasamshi gathas. Brhadaranyaka, Chandogya Upanishad, Gautama dharmasutras, Skandapurana, Bhagavata purana and other texts also refer to the Puranas. Mahabharata (Vana. Parv. 191.6) speaks of the Purana given by Vayu (Vayupurana).[15] The Puranas were written to bring the the teachings of the Vedas closer to the common man. They contain the essence of the Vedas.
सर्व वेदार्थ साराणि पुराणानि । sarva vēdārtha sārāṇi purāṇāni । (Nara. Pura. 1.9.100)
The Puranas have five characteristics (Pancha-Lakshana) viz., history, cosmology (with various symbolical illustrations of philosophical principles), secondary creation, genealogy of kings and of Manvantaras.
All the Puranas belong to the class of Suhrit-Sammitas (सुहृत्-सम्मित) or Mitra-sammita (मित्र-सम्मित). Vyasa is the compiler of the Puranas from age to age; and for this age, he is Krishnadvaipayana, the son of Parasara.
The aim of the Puranas is to impress on the minds of the masses the teachings of the Vedas and to generate in them devotion to deities and celestial beings, through concrete examples, stories, legends, lives of rishis, rajas, maharajas and great men, allegories and chronicles of great historical events. The seers made use of these to illustrate the eternal principles of religion. The Puranas were meant, not for the scholars, but for the ordinary people who could not understand deep philosophy and who could not study the Vedas.
The Darshanas propound complex and abstract thoughts which cannot be easily grasped. They are meant only for the learned few. Through Puranas, essential teachings are taught in a very easy and interesting way. Even to this day, the Puranas are popular. The Puranas contain the history of remote times. They also give a description of the regions of the universe not visible to the ordinary physical eye. They are very interesting to read and are full of information of all kinds.[5] Early commentators namely, Apararka, Ballalasena and Hemadri profusely quote the Puranas as the sources of dharma. Topics like Shraddha, Vratas, danas, shanti karmas, tirthas, rajadharmas are predominantly seen in the Matsya Purana. So also in the Vishnupurana, varnashramadharmas, panchamahayajnas, samskaras, nitya and naimittika karmas are extensively described.[15]
The Eighteen Mahapuranas
There are eighteen MahaPuranas and an equal number of subsidiary Puranas or Upa-Puranas. Vishnupurana (3.6.20 - 24) details the 18 Mahapuranas as follows[17]:
Padmapurana and Matsyapurana (Adhyaya 53[23]) mentions about the division of Sattvic Puranas (six), in praise of Vishnu (mokshaprada) are Vishnu, Narada, Bhagavata, Garuda, Padma and Varaha puranas. Six, in praise of Sarasvati and Brahma (svargaprada) are Rajasic, they include Brahma, Brahmanda, Brahmavaivarta, Markandeya, Bhavishya, Vamana. Six in praise of Shiva are Tamasic and they include Matsya, Kurma, Linga, Shiva, Skanda, Agni puranas.
Upapuranas
The Upa-puranas are similar in content to the 18 mahapuranas and they are written by many different seers.
- आद्यं सनत्कुमारोक्तं नारसिंहमथापरम् ॥ १,२२३.१७ ॥ तृतीयं स्कान्दमुद्दिष्टं कुमारेण तु भाषितम् । चतुर्थं शिवधर्माख्यं स्यान्नन्दीश्वरभाषितम् ॥ १,२२३.१८ ॥ दुर्वाससोक्तमाश्चर्यं नारदोक्तमतः परम् । कापिलं वामनञ्चैव तथैवोशनसेरितम् ॥ १,२२३.१९ ॥ ब्रह्माण्डं वारुणञ्चाथ कालिकाह्वयमेव च । माहेश्वरं तथा साम्बमेवं सर्वार्थसञ्चयम् । पराशरोक्तमपरं मारीचं भार्गवाह्वयम् ॥ १,२२३.२० ॥ पुराणं धर्मशास्त्रञ्च वेदास्त्वङ्गानि यन्मुने । (Garu. Pura. 1.223.17-20)[24]
- ādyaṁ sanatkumārōktaṁ nārasiṁhamathāparam ॥ 1,223.17 ॥ tr̥tīyaṁ skāndamuddiṣṭaṁ kumārēṇa tu bhāṣitam । caturthaṁ śivadharmākhyaṁ syānnandīśvarabhāṣitam ॥ 1,223.18 ॥ durvāsasōktamāścaryaṁ nāradōktamataḥ param । kāpilaṁ vāmanañcaiva tathaivōśanasēritam ॥ 1,223.19 ॥ brahmāṇḍaṁ vāruṇañcātha kālikāhvayamēva ca । māhēśvaraṁ tathā sāmbamēvaṁ sarvārthasañcayam । parāśarōktamaparaṁ mārīcaṁ bhārgavāhvayam ॥ 1,223.20 ॥ purāṇaṁ dharmaśāstrañca vēdāstvaṅgāni yanmunē । (Garu. Pura. 1.223.17-20)
According to Garuda Purana, Upapuranas include Sanathkumara, Narasimha, Skanda, Shivadharma, Ascharya purana, Narada, Nandi purana, Kapila, Vamana, Ushana, Brahmanda, Varuna, Kalika, Maheshvara, Samba, Parashara, Maricha, Bhargava puranas.
According to Swami Sivananda the Upa-puranas are: Sanat-kumara, Narasimha, Brihan-naradiya, Siva-rahasya, Durvasa, Kapila, Vamana, Bhargava, Varuna, Kalika, Samba, Nandi, Surya, Parasara, Vasishtha, Devi-Bhagavata, Ganesa, Mudgala, and Hamsa. The Ganesa and Mudgala Puranas are sectarian Upapuranas devoted to Ganesha.[5]
Thus, Upapuranas are said to be more recent, having names similar to those in Mahapuranas and deal not only with Shiva and Vishnu but also Surya, Shakti, Ganapati deities.[25]
Puranas Vs Sthala Puranas
Puranas are large ancient texts, included in the Chaturdasha vidyas different from the sthalapuranas which are not classified so. Sthalapuranas narrate the local legends and stories connected with a certain tirtha or temple (the word `Sthala` means `Place` in Samskrit). There are numerous Sthala Puranas, some having legends associated with locals in that place, some with references in samskrit literature. Many such local anecdotes and some of the Samskrit versions also appear in a Mahapurana or an Upapurana. Examples : Story of Bhakta Kannappa associated with Shiva temple in Srisailam (association of a local legend). Srisailam has a puranic references as one of the Jyotirlingas. Gokarna temple has the puranic legend of Shivalinga pratisha done by Ravanasura.
The Itihasas
Referred to as Epics, there are two books under this heading generally accepted by the scholars:
- Ramayana
- Mahabharata
These two epics embody all that is in the Vedas, but only in a simpler manner. These also belong to the category of Suhrit-Sammitas or the Friendly Treatises, while the Vedas are called the Prabhu-Sammitas or the Commanding Treatises with great authority.
These works explain the great universal truths in the form of historical narratives, stories and dialogues. These are very interesting volumes and are liked by all, from the inquisitive child to the intellectual scholar and have kept the Dharmik traditions alive through the ages of invasion and turmoil in Bharatavarsha. The Itihasas give us beautiful stories of absorbing interest and importance, through which all the fundamental teachings of Sanatana Dharma are impressed on one's mind. The laws of Smritis and the principles of the Vedas are stamped firmly on the minds of the people of Bharatavarsha through the noble and marvellous deeds of their great national heroes. We get a clear idea of Dharmas from these sublime stories. The awe-inspiring Brahman or Purusha expressed in high abstract philosophy of the Upanishads, Vedanta and the Brahma Sutras were brought closer to the educationists, warriors, a businessman, a farmer in the fields in an way intelligible to all of them. Hence, the compassionate seers Valmiki and Vyasa wrote the Itihasas for the benefit of common people. The same philosophy is presented with analogies and parables in a tasteful form to the common run of mankind.[5]
Ramayana and Mahabharata
The two well-known Itihasas (histories) are the epics (Mahakavyas), Ramayana and Mahabharata They are two very popular and useful Sastras of the Hindus. The Ramayana was written by the sage Valmiki, and the Mahabharata by Vyasa. The Ramayana and the Mahabharata speak to us clearly about the ancient India, about her people, her customs, her ways of living, her arts, her civilization and culture, her manufactures etc.[26]
| Ramayana | Mahabharata |
|---|---|
| It is called the Adikavya | It is called Panchamaveda |
| Contains the story of a single hero: Sri Rama | Contains many heroes : Kurus and Pandavas |
| Belongs to Parikriya (परिक्रिया) kind of Itihasa | Belongs to Purakalpa (पुराकल्पा) kind of Itihasa |
| Happened in the Tretayuga | Happened in the end of Dvaparayuga |
| Story of Avatara purusha - Sri Rama | Story of Avatara purusha - Sri Krishna |
| Story connected with 4 of Saptarishis - Atri, Bharadwaja, Vasishta and Visvamitra | No connection at all with any of the ancient rishis |
| Sri Rama's actions exemplified Dharma | Yudhisthira and Sri Krishna though followed Dharma were more routed in Rajaneeti |
| Filled with vivid descriptions | Such descriptions of natural beauty are less. |
| Rama's army included Vanaras or monkeys | Kurupandavas armies were vast and included mankind. |
Ramayana
The Ramayana, the Adi-Kavya or the first epic poem, relates the story of Sri Rama, the ideal man. It is the history of the family of the solar race descended from Ishvaku, in which was born Sri Ramachandra, the Avatara of Lord Vishnu, and his three brothers. The ideal characters such as Rama, Sita, Lakshmana, Bharata and Sri Hanuman that we find in Ramayana firmly establish Hindu Dharma in our minds. The story of the birth of Rama and his brothers, their education and marriages, the exile of Sri Rama, the carrying off and recovery of Sita, his wife, the destruction of Ravana, the Rakshasa King of Lanka, and the reign of Sri Rama, are described in detail in Ramayana. How a man should behave towards his superiors, equals and inferiors, how a king ought to rule his kingdom, how a man should lead his life in this world, how he can obtain his release, freedom and perfection, may be learnt from this epic.
The Ramayana gives a vivid picture of Indian Dharmik life. The lives of Rama, Bharata and Lakshmana provide a model of fraternal affection and mutual service. Sri Hanuman stands as an ideal unique Karma Yogin. The life of Sita is regarded as the most perfect example of womanly fidelity, chastity and affection. The Ramayana is written in twenty-four thousand slokas by Sri Valmiki Maharshi.[5] A few instances of topics of dharma dwelt on by Ramayana include : Rajadharma in Balakanda, Adhyaya 7, Ayodhyakanda, Adhyaya 100, Aranyakanda, Adhyaya 6, 9 and 33, 40, 41. Shraddha in Ayodhyakanda, Adhyaya 77, 103 and 111. Stridharma in Ayodhyakanda, Adhyaya 24, 26-27, 29, 39 etc. Ramayana forms the basis for the creation of volumes of Laukika Sahitya of future ages.(Page no 158 to 160 of Reference [15])
The Mahabharata
The Mahabharata is the history of the Pandavas and the Kauravas. It gives a description of the great war, the Battle of Kurukshetra, which broke out between the Kauravas and the Pandavas who were cousins and descendants of the lunar race. The Mahabharata is an encyclopaedia of Hindu Dharma. It is also called the fifth Veda. There is really no theme in religion, philosophy, mysticism and polity which this great epic does not touch and expound. It contains very noble moral teachings, useful lessons of all kinds, many beautiful stories and episodes, discourses, sermons, parables and dialogues which set forth the principles of morals and metaphysics. The Mahabharata contains also the immortal discourse of Bhishma on Dharma, which he gave to Yudhishthira, when he was lying on the bed of arrows. The whole Mahabharata forms an encyclopedia of history, morals and religion unsurpassed by any other epic in the world. The Pandavas obtained victory through the grace of Sri Krishna. The Mahabharata is written in one hundred thousand slokas by Sri Krishnadvaipayana Vyasa. Mahabharata draws extensively on the dharmashastras and a few instances are as follows,(Page no 158 to 160 of Reference [15])
- Arachaka (evils of anarchy) - Shantiparva, 40
- Ashrama dharmas - Shanti parva, 61, 243 to 246
- Achara - Anushasana parva, 104, and Asvamedhika parva, 45
- Dana - Vanaparva 186, Shanti parva 235, Anushasana parva 57-99
- Prayaschitta - Shanti 34-35, 165
- Rajaniti - Sabhaparva 5, Vanaparva 150, Udyogaparva 33 and 34, Shantiparva 65 and 297, Anushasana parva 48 and 49
- Varnadharma - Shantiparva 60 and 297
- Shraddha - Striparva 26 and 27, Anushasana parva 87 to 95
पञ्चमवेदः ॥ Panchamaveda
Though the general agreement about the number of vedas is four, there are instances in literature about Panchamaveda. However, in the four vedas the language and format of the writings are different from that of the Puranas and Itihasas which are called the Panchamaveda. Skanda Purana and Bhagavata purana[27][26] mention that Puranas and Itihasa constitute Panchamaveda while Bhavishya purana states that Mahabharata is called Panchamaveda[28]
Darshana Shastras
The ancient Indian thought process, the tattvas and siddhantas related to Sanatana Dharma are deeply dealt with in the six views or systems called as Shad Darshanas. Based on the Vedic knowledge, they are all designed to lead man to the One Science, the One Wisdom, which saw One Self as Real (Truth or Satya). They along with the Vedas and other Vaidika vangmaya are however classified as Apara vidya leading one to know the One Self (Atman) through the experience of Self which was called Para vidya. Since these shastras are founded accepting the authority of the Vedas they are called Astika darshanas. They are best understood when seen in relation with each other, thus revealing their Unity rather than when seen in opposition. The six Astika Darshanas or Shad Darshanas are[26]
Purva Mimamsa is commonly called as Mimamsa, while Uttara Mimamsa is called Vedanta. Each Darshana is associated with a rishi, a preceptor, who gives its principles in the form of Sutras or short terse sentences embedded with a great meaning in them. Thus the shastra lekhana paddhati or the writing format of shastras primarily involve the Sutras for which Bhashyam, a commentary and further on Vritti or Vartikas which are also explanatory notes are written by various authors. The object of all the darshanas is the same - to rescue men from sufferings of three kinds
The way to rescue propounded by these darshanas is also the same - removal of Avidya, which creates bandhana or bondage to Samsara, consequently union with the Supreme. The names used for Avidya, Ignorance, by different shastras are different but in essence all of them spell out the same situation of the mind. For example
- Nyaya calls it as Mithyajnana (मिथ्याज्ञानम्), false knowledge
- Sankhya calls it Aviveka (अविवेकः), non-discrimination between Self and Real.
- Yoga and Vedanta call it (अविद्या), incorrect knowledge
Each darshana aims at the removal of Ignorance by acquiring and internalizing or experiencing the Jnana, whereupon Ananda (आनन्दः) is enjoyed in the state termed as Moksha. Each of these darshanas establish their concepts by providing pramanas or proofs. Although, there are about ten kinds of pramanas primarily six kinds of them are accepted by the six darshana shastras, called as Shad Pramanas. Brief introduction of the six darshana shastras is given below[26][29]
| Darshana | Deals with | Rishi | Authoritative Bhashyam | Pramanas Accepted | Important Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nyaya Darshana | System of Logic | Gautama | Vatsyayana | Pratyaksha, Anumana, Upamana, Shabda | Sutras divided in five books.
Knowledge is divided into 16 Padarthas Asatkaryavada |
| Vaiseshika Darshana | System of Particulars | Kanada | Prashastapada | Pratyaksha, Anumana | Knowledge is divided into 6 Padarthas
Asatkaryavada |
| Samkhya Darshana | System of Numbers | Kapila | Samkhya Karika of Ishvara Krishna
Aniruddha Vijnanabhikshu |
Pratyaksha, Anumana
Aptavachana |
Dvaita siddhanta of Prakrti and Purusha and Viveka
Origin of the 25 principles - Mahat, Ahamkara, the Tanmatras and Purusha. Satkaryavada Nir-Isvaravada |
| Yoga Darshana | System of Effort or of Union | Patanjali | Vyasa bhashyam | Pratyaksha, Anumana, Shabda | Sutras are 198 arranged in 4 padas. Aim is chittavrtti virodha (stop the movements of Chitta or manas)
Sa-Ishvara Samkhya siddhantam |
| Mimamsa Darshana | System of Interpreting the Vedic texts | Jaimini | Shabara bhashyam | Prabhakara school : Pratyaksha, Anumana, Shabda, Upamana, Arthapatti
Kumarila school : 5 above and Abhava (totally 6) |
Concerned with karmakanda of the Veda. Mimamsa Sutras are divided into 12 books. |
| Vedanta | System of Interpreting the Vedic texts | Vyasa | 3 Schools : Advaita : Sri Shankaracharya Vishishtadvaita : Sri Ramanujam
Dvaita : Madhavacharya |
Advaita : 6 Pramanas
Vishishtadvaita and Dvaita : 3 pramanas (pratyaksha, anumana and shabda) |
Concerned with the jnanakanda of the Veda and Ishvara. Brahmasutras are important texts. |
Agamas
Agamas are a special class of literature, which include theological treatises and practical manuals of devata aradhana (worship) which have also been handed down through a succession of teachers from the ancient times.[30][31] However, Agama shastras are not part of the Vedas (which are also called Nigamas), and do not derive their authority directly from the Vedas neither are they antagonistic to Vedas. They are, in fact, vedic in spirit and character and use the veda mantras while performing the services. The Vedas explicitly do not discuss about pratima aradhana (idol worship). Agama texts support the view that Japa, Homa, Dhyana and Archa are the four methods to approach the divine and of these, the Agamas are based on Archa (worship). They describe primarily the procedure and rituals of deity worship, rather lay down the rules for a devata vigraha to be worship-worthy, thus are related to devata vigraha (imagery and iconography) and devalaya nirmana (temple construction).[32]
The icon and its form, the temple and its structure, the rituals and their details, thus get interrelated. [32]
They also give elaborate details about ontology and cosmology, liberation, devotion, meditation, philosophy of Mantras, mystic diagrams, charms and spells, temple-building, image-making, domestic observances, social rules, public festivals, etc.[5]
Agama is essentially a tradition (congregational, worship carried out in full public view) and Tantra is a technique (individualistic, carried out in quiet privacy, with self discipline and intensity), but both have similar ideology. Temple worship includes both Agama and Tantric worship sequences; several of them involving the devotees, while the tantric sequences are conducted by priests in the sanctum sanctorum away from public gaze. Agama worship methods of devatas include the rituals (Tantras), verbal chanting (Mantras) and through symbolic charts (Yantras). All the Agamas deal with 4 padas
- Jnana (Knowledge) includes the theological and spiritual aspects
- Yoga (Meditation) for mental discipline
- Kriya (Esoteric Ritual) lays the rules for temple construction and pratishta (consecration of deity)
- Charya (Ways of Worship) pertain to observing the achara vidhis (rituals) and festivals
The Agamas are divided into three sections: The Vaishnava, the Saiva and the Sakta. The three chief sects of Hinduism, viz., Vaishnavism, Saivism and Saktism, base their doctrines and dogmas on their respective Agamas.[5] The term Agama is used for the Vaishnava and Shaiva traditions, while those related to Shakti were termed as Tantric.
The Vaishnava Agamas are primarily of two kinds:[5]
- Vaikhanasa
- Pancharatra
The Brahma, Saiva Kaumara, Vasishtha, Kapila, Gautamiya and the Naradiya section of the Santi-Parva of the Mahabharata is the earliest source of information about the Pancharatras.
Vishnu is the Supreme Lord and the Pancharatra Agamas are believed to be revealed by Sri Mahavishnu Himself.
The Saiva Agamas
Less formal than the Vaishnavas, the Shaivas recognize twenty-eight Agamas, of which the chief is Kamika. The Agamas are the basis of Kashmir Saivism which is called the Pratyabhijna system. The latter works of Pratyabhijna system show a distinct leaning to Advaitism. The Southern Saivism, i.e., Saiva Siddhanta and the Kashmir Saivism, regard these Agamas as their authority, besides the Vedas. Shiva is the central deity in the Shaiva Agamas and they hold that the Ishana mukham of Shiva revealed the 28 agamas, while the other four faces of Shiva, namely Tatpurusha, Aghora, Vamadeva and Sadyojata revealed the four vedas. The 28 Agamas are placed in two categories :
The Sakta Agamas
There is another group of scriptures known as the Tantras. They belong to the Sakta cult. They glorify Sakti as the World-Mother. They dwell on the Sakti (energy) aspect of God and prescribe numerous courses of ritualistic worship of the Divine Mother in various forms. There are seventy-seven Agamas. These are very much like the Puranas in some respects. The texts are usually in the form of dialogues between Siva and Parvati. In some of these, Siva answers the questions put by Parvati, and in others, Parvati answers, Siva questioning. Mahanirvana, Kularnava, Kulasara, Prapanchasara, Tantraraja, Rudra-Yamala, Brahma-Yamala, Vishnu-Yamala and Todala Tantra are the important works.[5]
Sampradayas
The Vedic vision encompasses all fields of knowledge as everything and everyone is integral part of the Supreme. There are practically innumerable branches of the main three schools (Advaita, Vishistadvaita and Dvaita), called Sampradayas, generally categorized as Vaishnava, Shaiva, Shakta, and Smarta. These schools have developed independent literature over time after the particular preceptors who started or advocated the concepts.[5]
A Sampradaya is an ideological tradition in which a founder called as Acharya lays down some principles based mostly on the theological and darshanic concepts from Vedas and Vaidika vangmaya. These teachings are transmitted faithfully by his students who in turn became teachers after absorbing those principles and practices to perfection, self-realization and mastery. Any established set of theory and associated practices, forms a particular school of thought of the founder called as a Sampradaya and a traditional lineage of teachers from any Sampradaya is called Parampara. This concept applies at various levels and constitutes the basis of religious Institutions (or Mathas) founded by great Acharyas, and also the heritage of high level family traditions in the Hindu concept. [34]
We see since vedic period, often these two (religious affiliation and family descendence) are highly interconnected as Vedic knowledge makes no difference between son and pupil. Many times we see the student is mentioned in the rishi's lineage. In the case of religious affiliation, a disciple approaches a Sampradaya because he is attracted by the particular teachings, beliefs and practices characteristic to that tradition, and therefore accepts to become integrated into the system.
Sampradayas mostly have a diksha procedure, a formal initiation further to which a strict adherence to the instructions and a specific check-and-balance system ensures that the disciple follows the beliefs of the tradition thereby sustaining it. The current teacher has the right and duty to train the aspirant disciples as required, and will endorse them only when they have demonstrated the appropriate realizations in theory and practice, according to the various levels and positions in the Institution. Such endorsement comes in the form of appointment in various positions as preachers, leaders, and initiating teachers. Sampradayas may be classified based on the deities[34]
- SrimahaVishnu : Vaishnava Sampradayas have the greatest number of subsects.
- Shiva : Shaivite Sampradaya
- Devi : (Durga, Lakshmi, Saraswati) called Shakta Sampradaya
- Ganesh : Ganapatyas
- Skanda : Kaumaras
- Suryas : Sauras
Laukika Sahitya
These writings are extensive and a few important of them have been discussed as follows[5]
The Kavyas
These are highly scholarly compositions in poetry, prose or both. The greatest of poetical Kavyas are those of Kalidas (The Raghuvamsa and Kumarasambhav), Bharavi (The Kiratarjuniya), Magha (The Sisupalavadha), Sri Harsha (The Naishadha). The best prose Kavyas in the whole of Sanskrit literature were written by Bhattabana (The Kadambari and Harshacharita). Among those containing both poetry and prose, the Champu-Ramayana and the Champu-Bharata are most famous.
The Natakas
These are marvellously scholastic dramas embodying the Rasas of Sringara, Vira, Karuna, Adbhuta, Hasya, Bhayanaka, Vibhatsa and Raudra. The best dramas are written by Kalidasa (Sakuntala), Bhavabhuti (Uttara Rama-Charit), and Visakhadatta (Mudrarakshasa).
The Alankaras
The Alankaras are the grand rhetorical texts, that highlight the science of perfection and beauty of ornamental language, and of effective composition with elegance and force, both in poetry and in prose. These are the fundamentals of Sanskrit Sahitya, even superior to the Kavyas and the Natakas. The best Alankara-Granthas are those of Mammata (Kavyaprakasa) and Jagannatha (Rasagangudhara).
The Subhashitas
The Subhashitas are wise sayings, instructions and stories, either in poetry or in prose. Examples are Bhartrihari's three centuries of verses, the Subhashita-Ratna-Bhandagara and Somadeva Bhatta's Katha-Sarit-Sagara or Kshemendra's Brihat-Katha-Manjari. The Panchatantra and the Hitopadesa also belong to this category.
Verses and Meanings
Vishnupurana (3.6.20 - 24) details the 18 Mahapuranas as follows[17]
अष्टादश पुराणानि पुराणज्ञाः प्रचक्षते । ब्राह्मं पाद्मं वैष्णवञ्च शैवं भागवतं तथा ।। २० ।।
aṣṭādaśa purāṇāni purāṇajñāḥ pracakṣatē । brāhmaṁ pādmaṁ vaiṣṇavañca śaivaṁ bhāgavataṁ tathā ।। 20 ।।
अथान्यन्नारदीयञ्च मार्कण्डेयञ्च सप्तमम् । आग्नेयमष्टमञ्चैव भविष्यं नवमं तथा ।। २१ ।।
athānyannāradīyañca mārkaṇḍēyañca saptamam । āgnēyamaṣṭamañcaiva bhaviṣyaṁ navamaṁ tathā ।। 21 ।।
दशमं ब्रह्मवैवर्तं लैङ्गमेकादशं स्मृतम् । वाराहं द्वादशञ्चैव स्कान्दञ्चात्र त्रयोदशम् ।। २२ ।।
daśamaṁ brahmavaivartaṁ laiṅgamēkādaśaṁ smr̥tam । vārāhaṁ dvādaśañcaiva skāndañcātra trayōdaśam ।। 22 ।।
चतुर्दशं वामनञ्च कौर्मं पञ्चदशं स्मृतम् । मात्स्यञ्च गारुड़ञ्चैव ब्रह्माण्डञ्च ततः परम ।। २३ ।।
caturdaśaṁ vāmanañca kaurmaṁ pañcadaśaṁ smr̥tam । mātsyañca gāruḍa़ñcaiva brahmāṇḍañca tataḥ parama ।। 23 ।।
तथा चोपपुराणानि मुनिभिः कथितानि च । महापुराणान्येतानि ह्मष्टादश महामुने ।। २४ ।।
tathā cōpapurāṇāni munibhiḥ kathitāni ca । mahāpurāṇānyētāni hmaṣṭādaśa mahāmunē ।। 24 ।।
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 Gopal Reddy, Mudiganti and Sujata Reddy, Mudiganti (1997) Sanskrita Saahitya Charitra (Vaidika Vangmayam - Loukika Vangamayam, A critical approach) Hyderabad : P. S. Telugu University
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Venkateswara Rao. Potturi (2010) Paaramaathika Padakosam Hyderabad: Msko Books
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Shri. Kishore Mishra's Article : Vaidik Vangmay ka Shastriya Swaroop in Vedic Heritage Portal.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Manu Smrti (Adhyaya 12)
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 5.11 5.12 5.13 5.14 5.15 5.16 5.17 5.18 5.19 5.20 5.21 5.22 5.23 5.24 5.25 5.26 Swami Sivananda, All about Hinduism
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Malladi, Sri. Suryanarayana Sastry (1982) Samskruta Vangmaya Charitra, Volume 1 Vaidika Vangmayam Hyderabad : Andhra Sarasvata Parishad
- ↑ Introduction to Samhitas in Vedic Heritage Portal
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Sharma, Ram Murthy. (1987 2nd edition) Vaidik Sahitya ka Itihas Delhi : Eastern Book Linkers
- ↑ Adhikari, Shriram Article : Samaved ka parichay evam vaisishtya from Vedic Heritage Portal
- ↑ Dr. Shashi Tiwari, Sanskrit Department, Delhi University in the Introduction of Brahmanas (Vedic Heritage Portal)
- ↑ Dr. Shashi Tiwari, Sanskrit Department, Delhi University on Introduction to Aranyakas in Vedic Heritage Portal
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Raghunathacharya, S. B. (1985) Arshavijnana Sarvasvamu, Volume 2 : Brahmanalu (Telugu) Tirupati : Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanam
- ↑ Poola, Tirupati Raju (1985), Structural Depths of Indian Thought. USA: State University of New York Press, ISBN 978-0887061394, pages 35-36
- ↑ Taittriya Aranyaka (Prapathaka 1 Anuvaka 2)
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 15.4 15.5 15.6 Kane, Pandurang. Vaman. (1930) History of Dharmasastra, Volume One. Poona: Bhandarkar Oriental Research Institute
- ↑ Shri, Satya. (2017) Demystifying Brahminism and Reinventing Hinduism: Vol 1. Chennai: Notion Press
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 Vishnupurana (Amsha 3 Adhyaya 6)
- ↑ Manu Smrti (Adhyaya 2)
- ↑ R. Suresha, (2009) Ph. D Thesis Titled : Learning systems in Ancient Sanskrit - A Critical Study. Mangalore University
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Sri Sri Sri Chandrasekharendra Saraswathi Swamiji, (2000) Hindu Dharma (Collection of Swamiji's Speeches between 1907 to 1994)Mumbai : Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan
- ↑ Yajnavalkya Smrti (Adhyaya 1 Acharaadhyaya)
- ↑ Pt. Ramnarayandatt Shastri, Mahabharata by Maharshi Vedavyasa , Volume 5, Shanti Parva. Gorakhpur : Gita Press
- ↑ Matsya Purana (Adhyaya 53)
- ↑ Garuda Purana (Acharakanda Adhyaya 223)
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Malladi, Sri. Suryanarayana Sastry (1982) Samskruta Vangmaya Charitra, Volume 2 Laukika Vangmayam Hyderabad : Andhra Sarasvata Parishad
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 26.3 Sanatana Dharma : An Advanced Textbook of Hindu Religion and Ethics. (1903) Benares : The Board of Trustees, Central Hindu College
- ↑ Shrimad Bhagavata Puranam (Skanda 1 Adhyaya 4)
- ↑ Upadhyaya, Baburam. (2012) Bhavishya Mahapurana with Hindi Translation Volume 1 Brahmaparva. Prayag : Hindi Sahitya Sammelan
- ↑ Sinha, Nandalal (1915) The Sacred Books of the Hindus : The Samkhya Philosophy. (Volume XI). Allahabad : The Panini Office
- ↑ J. Padmamalini, (2015) Ph. D Thesis Titled : Sri Prasanna Venkateswara Swamy Temple of Appalayagunta An Agamic Study Tirupati : Sri Venkateswara University
- ↑ S, Veerabhadra.(2016) Ph. D Thesis Titled : Vishnu Iconography in Andhra During the Vijayanagara period. Tirupati : Sri Venkateswara University.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 Saligrama Krishna Ramachandra Rao. Agama Shastra and Temple Worship. Extract from : The agama Encyclopaedia 12 Vols.; Revised Edition of Agama Kosa
- ↑ M. Arunachalam, (1983) The Saivagamas. Madras : Kalakshetra Publications Press.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 Parama Karuna Devi, (2009) Puri, The Home of Lord Jagannatha. Puri :Jagannatha Vallabha Research Center