Difference between revisions of "Mercury or Parada (पारद)"
(added content) |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
The rasa (taste), Virya (potency) and Vipaka (taste at the end of digestion) of Mercury has been quoted as similar to ambrosia in Rasarnavam. Mercury possesses all the qualities of Animadi astaguna (eight qualities) which are required for the accomplishments of human life. There is no other thing in the earth than Mercury to attain salvation. It imparts glory to human body by eradicating old age according to the text Rasendra mangalam by Kaviraja H. S. Sharma.<ref name=":0" /> Mercury is regarded as a heavy metal that contains a variety of impurities and has poisonous and harmful effects on the body if it is not well purified.<ref>Dadu, Vaibhav. (2016) Philosophical Tenets of Vaiseshika and the fundamentals of Ayurveda World Journal of Pharmaceutical </ref> | The rasa (taste), Virya (potency) and Vipaka (taste at the end of digestion) of Mercury has been quoted as similar to ambrosia in Rasarnavam. Mercury possesses all the qualities of Animadi astaguna (eight qualities) which are required for the accomplishments of human life. There is no other thing in the earth than Mercury to attain salvation. It imparts glory to human body by eradicating old age according to the text Rasendra mangalam by Kaviraja H. S. Sharma.<ref name=":0" /> Mercury is regarded as a heavy metal that contains a variety of impurities and has poisonous and harmful effects on the body if it is not well purified.<ref>Dadu, Vaibhav. (2016) Philosophical Tenets of Vaiseshika and the fundamentals of Ayurveda World Journal of Pharmaceutical </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In India, vermilion or cinnabar i.e. mercuric sulphide has had great ritual significance, typically having been used to make the red bindi or dot on the forehead usually associated with Hinduism.<ref>Srinivasan, Sharada and Ranganathan, Srinivasa. (2013) ''[http://eprints.nias.res.in/374/1/B8-2013%20Minerals%20and%20Metals%20Heritage%20of%20India.pdf Minerals and Metals Heritage of India].'' Bangalore:National Institute of Advanced Studies.</ref> | ||
== पर्यायाः ॥ Synonyms of Parada used in Ayurveda == | == पर्यायाः ॥ Synonyms of Parada used in Ayurveda == | ||
| − | According to Rasatarangini<ref name=":1">Kashinath Shastri (1986 reprint) ed., ''Ras Tarangini Of Sadananda Sharma With Prasadani Explanation Of Haridatt Shastri And Ras Vigyan Hindi Tika Of Dharmanand Shastri''. Delhi: Motilal Banarsidas (pp. | + | According to Rasatarangini<ref name=":1">Kashinath Shastri (1986 reprint) ed., ''Ras Tarangini Of Sadananda Sharma With Prasadani Explanation Of Haridatt Shastri And Ras Vigyan Hindi Tika Of Dharmanand Shastri''. Delhi: Motilal Banarsidas (pp. 71- )</ref>, the alternative names used for Pārada are <blockquote>रसो रसेन्द्रः सूतश्च रसेशश्च रसेश्वरः । चपलो रसराजश्च पारदश्च शिवाह्वयः ॥ १ ॥ (Rasa. Tara. 5.1) |
rasō rasēndraḥ sūtaśca rasēśaśca rasēśvaraḥ | capalō rasarājaśca pāradaśca śivāhvayaḥ || 1 ||</blockquote>The synonyms for mercury include rasa (रसः) rasēndraḥ (रसेन्द्रः) sūta (सूतः) rasēśa (रसेशः) rasēśvaraḥ (रसेश्वरः) capalā (चपलः) rasarāja (रसराजः) pārada (पारदः) śivāhvayaḥ (शिवाह्वयः - used in the sense of all the words meaning Shiva). The names given also explain the characteristics of the metal mercury.<ref name=":1" /> | rasō rasēndraḥ sūtaśca rasēśaśca rasēśvaraḥ | capalō rasarājaśca pāradaśca śivāhvayaḥ || 1 ||</blockquote>The synonyms for mercury include rasa (रसः) rasēndraḥ (रसेन्द्रः) sūta (सूतः) rasēśa (रसेशः) rasēśvaraḥ (रसेश्वरः) capalā (चपलः) rasarāja (रसराजः) pārada (पारदः) śivāhvayaḥ (शिवाह्वयः - used in the sense of all the words meaning Shiva). The names given also explain the characteristics of the metal mercury.<ref name=":1" /> | ||
| − | In Rasatarangini, we find the explanation of what each term means in its usage. <blockquote>रसनादभ्रकादीनां धातूनां कीर्तितो रसः । अभ्रकाद्यधिराजत्वाद्रसेन्द्र इति कथ्यते ॥२॥ (Rasa. Tara. 5.2) | + | In Rasatarangini, we find the explanation of what each term means in its usage. <blockquote>रसनादभ्रकादीनां धातूनां कीर्तितो रसः । अभ्रकाद्यधिराजत्वाद्रसेन्द्र इति कथ्यते ॥२॥ (Rasa. Tara. 5.2) rasanādabhrakādīnāṁ dhātūnāṁ kīrtitō rasaḥ | abhrakādyadhirājatvādrasēndra iti kathyatē ||2||</blockquote>Because mercury dissolves ('eats' or'engulfs') the maharasas such as Abhrakadi (mica) rasas etc, gold etc dhatus, it is called Rasa.<ref name=":2" /> As it is superior among Abhraka etc, it is called Rasendra.<ref name=":1" /> <blockquote>देहलोहभयीं सिद्धिं सूतेऽतः सूत उच्यते । स्वभावाच्चपलो यस्मात् ततोऽसौ चपलः स्मृतः ॥३॥ (Rasa. Tara. 5.3) dēhalōhabhayīṁ siddhiṁ sūtē’taḥ sūta ucyatē | svabhāvāccapalō yasmāt tatō’sau capalaḥ smr̥taḥ ||3|| </blockquote>As it brings about wellbeing in the body and is used in the preparation of gold etc dhatus, it is called Suta. By nature, it is mobile/moving hence called Chapala.<ref name=":1" /> <blockquote>आतङ्कपङ्कमग्नानां पारदानाच्च पारदः। अभ्रादिरसराजत्वाद्रसराजः स्मृतो बुधैः ॥४॥ (Rasa. Tara. 5.4) ātaṅkapaṅkamagnānāṁ pāradānācca pāradaḥ| abhrādirasarājatvādrasarājaḥ smr̥tō budhaiḥ ||4|| </blockquote>That which uplifts beings enmeshed in the dirt called roga/illness it is called Pārada. As a king (superior by qualities) among Ambhraka etc great aushadhis it is called Rasaraja.<ref name=":1" /> |
| − | + | == ऊत्पत्ति इतिहासश्च ॥ Origin and History == | |
| + | Parada has been referred to as having divine origin, associated with the deity Shiva or Hara in ancient literature (Rasa Ratna Samucchaya 1.61-68).<ref name=":6">Shankarlal Harishankar, (2019) ed. ''[https://archive.org/details/rasa-ratna-samucchaya-of-vagbhatacharya-shankar-lal-hari-shankar/page/n79/mode/2up Rasaratna Sammuchhaya by Acharya Vagbhata]'' Bombay: Khemraj Srikrishnadas Prakashan</ref> On the mountains of Himalayas, Shiva and his consort Parvati, engaged in intense sensual activities with a desire to win over the other. Devatas desired that Shiva and Parvati produce a son who could kill Tarakasura, but those activities caused a great disturbance upsetting the three worlds. However, seeing the brilliance of the raja and virya (of Parvati and Shiva) that was very powerful, sent Agni to cause a disturbance in the divine sensual activity. Agni went into the caves in the form of a pigeon and seeing him Shiva with great shyness realized that it was not a bird but was Agni and stopped the activity. By then the semen ejaculated which Shiva flung upon Agni. Unable to bear the tejas of the virya, Agni entered the waters of the Ganga. Soon Ganga was unable to bear the divine tejas which heated up the waters, so she washed ashore both Agni and the virya of Shiva. Due to the blemishes of the virya, metals of various kinds materialized on the banks of Ganga. At five places, where the virya dropped from Agni's mouth, there sprung five deep wells each having one of the five kinds of Parada. <blockquote>रासो रसेन्द्रः सूतश्च पारदो मिश्रकस्तथा । rāsō rasēndraḥ sūtaśca pāradō miśrakastathā | (Rasa. Ratn. Samu. 1.68)<ref name=":6" /></blockquote>They are Rasa, Rasendra, Suta, Parada and Mishraka. | ||
| − | + | The metal mercury was known to the Indians since ancient times. The Chinese and Egyptians considered it as a magic substance. Prof. J.A. Brown was the scientist who grouped this fluid metal among metals. The English name of this metal is based on the planet Mercury which is named after a swift messenger in Greek mythology. | |
| − | + | == स्वरूपम् ॥ Characteristics == | |
| + | Mercury is available in native and ore forms. Mercury is the only elemental metal that is liquid at room temperature. Mercury is silvery white, slowly tarnishes in moist air, and freezes into a soft solid like tin or lead at −38.83 °C (−37.89 °F). It boils at 356.62 °C (673.91 °F). It is a rather poor conductor of heat but a fair conductor of electricity. It alloys with copper, tin, and zinc to form amalgams, or liquid alloys. An amalgam with silver is used as a filling in dentistry. Mercury does not wet glass or cling to it, and this property, coupled with its rapid and uniform volume expansion throughout its liquid range, made it useful in thermometers.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
| − | + | According to Ayurveda texts<blockquote>अन्तसुनीलो बहिरुज्ज्वलो यो मध्यान्हसूर्यप्रतिमप्रकाशः । शस्तोऽध धूम्रः परिपाण्डुराश्च चित्रो न योज्यो रसकर्मासिद्धौ ॥ (Rasendramangala and Rasendrasara sangraha 1.9) | |
| − | + | ||
| + | antasunīlō bahirujjvalō yō madhyānhasūryapratimaprakāśaḥ | śastō’dha dhūmraḥ paripāṇḍurāśca citrō na yōjyō rasakarmāsiddhau || (Rasendramangala and Rasendrasara sangraha 1.9) | ||
| + | |||
| + | शुद्धः सूतो यतस्त्वन्तः सूनीलो बहिरुञ्ञ्बलः । सूयप्रभश्चाविशुद्धो धुम्रो वा परिपाण्डुरः ।।५॥ (Rasa. Tara. 5.5) | ||
| + | |||
| + | śuddhaḥ sūtō yatastvantaḥ sūnīlō bahiruññbalaḥ | sūyaprabhaścāviśuddhō dhumrō vā paripāṇḍuraḥ ||5|| (Rasa. Tara. 5.5)</blockquote>Parada which is outwardly shinning like the mid-day sun and having the hues of blue color internally is to be used and that Parada having dhumra varna (smoky hue), panduvarna (slight yellow hue) or chitra varna should not be used for preparation of aushadhis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == पारदस्य नैसर्गिकस्त्रोताः ॥ Natural Sources of Mercury == | ||
| + | Mercury occurs in Earth’s crust on the average of about 0.08 gram (0.003 ounce) per ton of rock. As mercury is in the liquid state at room temperature, it is termed as Galadrupyanibham (liquid silver) or Quick Silver. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Extremely rare natural alloys of mercury have also been found: moschellandsbergite (with silver), potarite (with palladium), and gold amalgam. Over 90 percent of the world’s supply of mercury comes from China; it is often a by-product of gold mining. China, Kyrgyzstan, and Chile are the leading producers of Mercury in the world.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === प्राप्तिस्थानम् ॥ Place of Availability === | ||
| + | Native mercury occurs in isolated drops and occasionally in larger fluid masses, usually with cinnabar, near volcanoes or hot springs. It is available generally in small globule form, situated in the deep holes in earth crust. Native mercury is available in USA in California, Almaden (Spain), Peru, Italy, New Zealand, Ukraine, Turkey, Brazil, Columbia, Equador apart from a few other places.<ref name=":3" /><ref name=":2" /> | ||
| − | + | === Ores of Mercury === | |
| + | Cinnabar, mercury sulfide (HgS), is the chief ore mineral of mercury. It is commonly encountered with pyrite, marcasite, and stibnite in veins near recent volcanic rocks and in hot-springs deposits. The most important deposit is at Almadén, Spain, where it has been mined for 2,000 years.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
| − | + | * Sulphide Ores | |
| + | ** Cinnabar (HgS) or Hingula | ||
| + | ** Metacinnabar (β-HgS) | ||
| + | ** Living Stonite (HgS 2Sb<sub>2</sub>S<sub>3</sub>) | ||
| + | * Chloride Ore | ||
| + | ** Calomel (Hg<sub>2</sub>Cl<sub>2</sub>) | ||
| + | * Oxide Ore | ||
| + | ** Monotroydite (HgO) | ||
| − | == | + | == रासभेदाः ॥ Types of Parada == |
In Rasaratna samucchaya,<ref name=":6" /> we find the following synonymous terms Rasa, Rasendra, Suta, Parada and Mishraka described as the five kinds of Parada.<blockquote>रासो रसेन्द्रः सूतश्च पारदो मिश्रकस्तथा । इति पञ्चविधो जातः क्षेत्रभेदेन शम्भुजः॥ (Rasa. Ratn. Samu. 1.68)<ref name=":6" /> rāsō rasēndraḥ sūtaśca pāradō miśrakastathā | iti pañcavidhō jātaḥ kṣētrabhēdēna śambhujaḥ|| </blockquote>Their qualities are also well described in the above text (Rasa. Ratn. Samu. 1.69-75)<ref name=":6" /> | In Rasaratna samucchaya,<ref name=":6" /> we find the following synonymous terms Rasa, Rasendra, Suta, Parada and Mishraka described as the five kinds of Parada.<blockquote>रासो रसेन्द्रः सूतश्च पारदो मिश्रकस्तथा । इति पञ्चविधो जातः क्षेत्रभेदेन शम्भुजः॥ (Rasa. Ratn. Samu. 1.68)<ref name=":6" /> rāsō rasēndraḥ sūtaśca pāradō miśrakastathā | iti pañcavidhō jātaḥ kṣētrabhēdēna śambhujaḥ|| </blockquote>Their qualities are also well described in the above text (Rasa. Ratn. Samu. 1.69-75)<ref name=":6" /> | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 72: | Line 97: | ||
# '''Daivatva''' include Trinetra, Harabeejam, Shiva, Shivaveerya, Skanda, Harateja, Rudraja, Deva etc. | # '''Daivatva''' include Trinetra, Harabeejam, Shiva, Shivaveerya, Skanda, Harateja, Rudraja, Deva etc. | ||
| − | == | + | == Properties and Uses of Parada == |
| − | Mercury | + | |
| + | === Physical Properties === | ||
| + | Mercury (Hg) has a unique combination of physical properties. Its low melting point and boiling point, high specific gravity (13.5 grams per cubic centimetre), uniform volume expansion over the entire range of temperatures in its liquid state, and high surface tension (so that it does not wet glass) make it useful for the measurement of temperature in thermometers and of pressure in barometers and manometers. In addition, the high electrical conductivity of liquid mercury has led to its use in sealed electric switches and relays, industrial power rectifiers, fluorescent and mercury-vapour lamps, mercury cell batteries, and as moving cathodes in the large-scale production of chlorine and caustic soda. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+Properties of the element Mercury<ref>https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/80/mercury</ref> | ||
| + | !atomic number | ||
| + | |80 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !atomic weight | ||
| + | |200.592 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !State at 20 °C | ||
| + | |Liquid | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Solidifying point | ||
| + | |39 °C | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !melting point | ||
| + | |−38.829°C, (−37.892°F) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !boiling point | ||
| + | |356.619°C, (673.914°F) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Specific Gravity | ||
| + | |13.6 grams/cm<sup>3</sup> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !'''oxidation states''' | ||
| + | | +1, +2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !electron configuration | ||
| + | |[Xe] 4f<sup>14</sup>5d<sup>10</sup>6s<sup>2</sup> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Pharmacological Properties === | ||
| + | Most of Rasa formulations have mercury as an important ingredient. Unpurified mercury has many toxic effects such as severe gastrointestinal irritations, peripheral circulatory collapse, metallic taste in mouth, excessive salivation, inflammation of gums, etc. Almost all classical texts related to Rasa Shastra (Ayurveda pharmaceutics for metalo-mineral preparations) have emphasized Parada Shodhana (purifying process of mercury) but with a variety of methods. These methods need to be revalidated with comprehensive methodology to develop its standard operative procedure (SOP), because standardization of the drugs is very crucial to ensure quality, efficacy, and reproducibility. Hence, Shodhana (purifying process), Mardana (trituration), Marana (incineration), Jarana (polling), Murchchna (process to put in disease curing capacity), etc., with herbomineral drugs are to be carried out as appropriate to receive the therapeutic benefits of Parada.<ref>Bhinde SS, Patgiri BJ. ''Quantification of mercury after Samanya Shodhana (purifying process): A preliminary analysis.'' J Drug Res Ayurvedic Sci 2022;6:65-71.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Although mercury compounds are regarded as poisonous, cinnabar (mercuric sulphide) is subjected to eighteen complex processes called ''samskāras'', including rubbing with various medicinally efficacious plant juices and extracts, incorporation of sulphur, mica, certain alkaline substances, etc. The resulting mercury compound was then declared fit for consumption and believed to lead to the body’s rejuvenation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Uses of Mercury === | ||
| + | Based on the utility of drugs in processing of Parada, they are classified in to Maharasa, Uparasa and Sadharana rasa. Maharasas have wide therapeutic utility and they are used / prescribed along with parada. They are also utilized in various samskaras of parada. Mercurial preparations are used in Pandu (anemia), Shwasa (dysapoea), Kasa (cough), Kamala (jaundice), Jwara (fever), Shula (spasmodic pain), Mutrakriccha (nephritis), Vamana (vomiting), Udara Pida (acute abdominal pain), Krimi Dosha (worm infestation), Atisara (diarrhea), etc.<ref>Sarkar, P.K., Das, Sanjita, Prajapati, P. K. (2010) ''Ancient concept of metal pharmacology based on Ayurvedic Literature'' Ancient Science of Life, Vol. 29, 4; pp1-6</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == पारदस्य नेसर्गिका दोषाः ॥ Doshas or Impurities of Parada == | ||
| + | According to Rasatarangini, Parada | ||
| + | |||
| + | नागवङ्गौ वह्निमलौ चापल्यं गरलं गिरिः । असह्याग्निश्च विज्ञेयो दोषा नैसर्गिका रसे ॥७॥ nāgavaṅgau vahnimalau cāpalyaṁ garalaṁ giriḥ | asahyāgniśca vijñēyō dōṣā naisargikā rasē ||7|| | ||
| + | |||
| + | नागाद् व्रणं भवेत्कुष्ठं वङ्गात्तापोऽग्निदोषतः । मलाज्जड्यं तु चापल्याद् बोजनाशो विषान्मृतिः ।॥८॥ nāgād vraṇaṁ bhavētkuṣṭhaṁ vaṅgāttāpō’gnidōṣataḥ | malājjaḍyaṁ tu cāpalyād bōjanāśō viṣānmr̥tiḥ |||8|| | ||
| + | |||
| + | गिरेः स्फोटोऽथ मोहश्च ह्यसह्याग्नेः प्रजायते । एतैर्दोषैर्विहीनञ्च रसेन्द्रमिह योजयेत् ॥ ९॥ girēḥ sphōṭō’tha mōhaśca hyasahyāgnēḥ prajāyatē | ētairdōṣairvihīnañca rasēndramiha yōjayēt || 9|| (Rasa. Tara. 5.7-9)<ref name=":1" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Intrinsically, Parada contains eight doshas namely, नाग (naga), वङ्ग (vanga), वह्नि (vahni), मल (mala), चापल्य (chapala), विष (visha), गिरि (giri), असह्याग्नि (asahyagni) | ||
| − | + | Though many Doshas are attributed to Mercury, Naga (Lead), Vanga (Tin) Doshas are considered the major ones. | |
== Mercury Poisoning == | == Mercury Poisoning == | ||
Revision as of 23:27, 26 October 2024
Pārada (Samskrit: पारदः), as mentioned in various Rasashastra texts of ancient India, means Mercury in English. It is a chemical element with atomic number 80 and chemical formula 'Hg (Hydrargyrum)'. Mercury (Hg), a metallic chemical element belonging to the zinc group (Group 12 [IIb] of the periodic table), is the only elemental metal that is liquid at room temperature. Mercury is silvery white, slowly tarnishes in moist air, and freezes into a soft solid like tin or lead at −38.83 °C (−37.89 °F). The chemical symbol Hg derives from the Latin hydrargyrum, “liquid silver.”[1] It is also called Quick Silver, as it appears like silver having the property of flowing.
According to Ayurveda Rasashastra, Rasa (रस) is the term used to denote Parada. Mercury is one of the metals which attracted wide attention of ayurvedic chemists and physicians.[2]
परिचयः ॥ Introduction
Parada (mercury-Hg) is one of the important core ingredients in Rasa (metals and minerals) Aushadhi (medicine). Most of Rasa formulations have mercury as an important ingredient. It is evident that raw mercury has many toxic effects such as severe gastrointestinal irritations, peripheral circulatory collapse, metallic taste in mouth, excessive salivation, inflammation of gums, etc.[3] But Mercury has therapeutic qualities similar to that of ambrosia. Mercurial medications prepared from purified Mercury can readily treat even Asadhya rogas (incurable diseases). Thus, Parada (Mercury) is the heart of Rasasastra. Recent world wide discussions on hazardous nature of Mercury have led to the global ban on Mercury. through the Minamata Convention, a global treaty on Mercury.[4]
The rasa (taste), Virya (potency) and Vipaka (taste at the end of digestion) of Mercury has been quoted as similar to ambrosia in Rasarnavam. Mercury possesses all the qualities of Animadi astaguna (eight qualities) which are required for the accomplishments of human life. There is no other thing in the earth than Mercury to attain salvation. It imparts glory to human body by eradicating old age according to the text Rasendra mangalam by Kaviraja H. S. Sharma.[4] Mercury is regarded as a heavy metal that contains a variety of impurities and has poisonous and harmful effects on the body if it is not well purified.[5]
In India, vermilion or cinnabar i.e. mercuric sulphide has had great ritual significance, typically having been used to make the red bindi or dot on the forehead usually associated with Hinduism.[6]
पर्यायाः ॥ Synonyms of Parada used in Ayurveda
According to Rasatarangini[7], the alternative names used for Pārada are
रसो रसेन्द्रः सूतश्च रसेशश्च रसेश्वरः । चपलो रसराजश्च पारदश्च शिवाह्वयः ॥ १ ॥ (Rasa. Tara. 5.1) rasō rasēndraḥ sūtaśca rasēśaśca rasēśvaraḥ | capalō rasarājaśca pāradaśca śivāhvayaḥ || 1 ||
The synonyms for mercury include rasa (रसः) rasēndraḥ (रसेन्द्रः) sūta (सूतः) rasēśa (रसेशः) rasēśvaraḥ (रसेश्वरः) capalā (चपलः) rasarāja (रसराजः) pārada (पारदः) śivāhvayaḥ (शिवाह्वयः - used in the sense of all the words meaning Shiva). The names given also explain the characteristics of the metal mercury.[7] In Rasatarangini, we find the explanation of what each term means in its usage.
रसनादभ्रकादीनां धातूनां कीर्तितो रसः । अभ्रकाद्यधिराजत्वाद्रसेन्द्र इति कथ्यते ॥२॥ (Rasa. Tara. 5.2) rasanādabhrakādīnāṁ dhātūnāṁ kīrtitō rasaḥ | abhrakādyadhirājatvādrasēndra iti kathyatē ||2||
Because mercury dissolves ('eats' or'engulfs') the maharasas such as Abhrakadi (mica) rasas etc, gold etc dhatus, it is called Rasa.[2] As it is superior among Abhraka etc, it is called Rasendra.[7]
देहलोहभयीं सिद्धिं सूतेऽतः सूत उच्यते । स्वभावाच्चपलो यस्मात् ततोऽसौ चपलः स्मृतः ॥३॥ (Rasa. Tara. 5.3) dēhalōhabhayīṁ siddhiṁ sūtē’taḥ sūta ucyatē | svabhāvāccapalō yasmāt tatō’sau capalaḥ smr̥taḥ ||3||
As it brings about wellbeing in the body and is used in the preparation of gold etc dhatus, it is called Suta. By nature, it is mobile/moving hence called Chapala.[7]
आतङ्कपङ्कमग्नानां पारदानाच्च पारदः। अभ्रादिरसराजत्वाद्रसराजः स्मृतो बुधैः ॥४॥ (Rasa. Tara. 5.4) ātaṅkapaṅkamagnānāṁ pāradānācca pāradaḥ| abhrādirasarājatvādrasarājaḥ smr̥tō budhaiḥ ||4||
That which uplifts beings enmeshed in the dirt called roga/illness it is called Pārada. As a king (superior by qualities) among Ambhraka etc great aushadhis it is called Rasaraja.[7]
ऊत्पत्ति इतिहासश्च ॥ Origin and History
Parada has been referred to as having divine origin, associated with the deity Shiva or Hara in ancient literature (Rasa Ratna Samucchaya 1.61-68).[8] On the mountains of Himalayas, Shiva and his consort Parvati, engaged in intense sensual activities with a desire to win over the other. Devatas desired that Shiva and Parvati produce a son who could kill Tarakasura, but those activities caused a great disturbance upsetting the three worlds. However, seeing the brilliance of the raja and virya (of Parvati and Shiva) that was very powerful, sent Agni to cause a disturbance in the divine sensual activity. Agni went into the caves in the form of a pigeon and seeing him Shiva with great shyness realized that it was not a bird but was Agni and stopped the activity. By then the semen ejaculated which Shiva flung upon Agni. Unable to bear the tejas of the virya, Agni entered the waters of the Ganga. Soon Ganga was unable to bear the divine tejas which heated up the waters, so she washed ashore both Agni and the virya of Shiva. Due to the blemishes of the virya, metals of various kinds materialized on the banks of Ganga. At five places, where the virya dropped from Agni's mouth, there sprung five deep wells each having one of the five kinds of Parada.
रासो रसेन्द्रः सूतश्च पारदो मिश्रकस्तथा । rāsō rasēndraḥ sūtaśca pāradō miśrakastathā | (Rasa. Ratn. Samu. 1.68)[8]
They are Rasa, Rasendra, Suta, Parada and Mishraka.
The metal mercury was known to the Indians since ancient times. The Chinese and Egyptians considered it as a magic substance. Prof. J.A. Brown was the scientist who grouped this fluid metal among metals. The English name of this metal is based on the planet Mercury which is named after a swift messenger in Greek mythology.
स्वरूपम् ॥ Characteristics
Mercury is available in native and ore forms. Mercury is the only elemental metal that is liquid at room temperature. Mercury is silvery white, slowly tarnishes in moist air, and freezes into a soft solid like tin or lead at −38.83 °C (−37.89 °F). It boils at 356.62 °C (673.91 °F). It is a rather poor conductor of heat but a fair conductor of electricity. It alloys with copper, tin, and zinc to form amalgams, or liquid alloys. An amalgam with silver is used as a filling in dentistry. Mercury does not wet glass or cling to it, and this property, coupled with its rapid and uniform volume expansion throughout its liquid range, made it useful in thermometers.[1]
According to Ayurveda texts
अन्तसुनीलो बहिरुज्ज्वलो यो मध्यान्हसूर्यप्रतिमप्रकाशः । शस्तोऽध धूम्रः परिपाण्डुराश्च चित्रो न योज्यो रसकर्मासिद्धौ ॥ (Rasendramangala and Rasendrasara sangraha 1.9)
antasunīlō bahirujjvalō yō madhyānhasūryapratimaprakāśaḥ | śastō’dha dhūmraḥ paripāṇḍurāśca citrō na yōjyō rasakarmāsiddhau || (Rasendramangala and Rasendrasara sangraha 1.9)
शुद्धः सूतो यतस्त्वन्तः सूनीलो बहिरुञ्ञ्बलः । सूयप्रभश्चाविशुद्धो धुम्रो वा परिपाण्डुरः ।।५॥ (Rasa. Tara. 5.5)
śuddhaḥ sūtō yatastvantaḥ sūnīlō bahiruññbalaḥ | sūyaprabhaścāviśuddhō dhumrō vā paripāṇḍuraḥ ||5|| (Rasa. Tara. 5.5)
Parada which is outwardly shinning like the mid-day sun and having the hues of blue color internally is to be used and that Parada having dhumra varna (smoky hue), panduvarna (slight yellow hue) or chitra varna should not be used for preparation of aushadhis.
पारदस्य नैसर्गिकस्त्रोताः ॥ Natural Sources of Mercury
Mercury occurs in Earth’s crust on the average of about 0.08 gram (0.003 ounce) per ton of rock. As mercury is in the liquid state at room temperature, it is termed as Galadrupyanibham (liquid silver) or Quick Silver.
Extremely rare natural alloys of mercury have also been found: moschellandsbergite (with silver), potarite (with palladium), and gold amalgam. Over 90 percent of the world’s supply of mercury comes from China; it is often a by-product of gold mining. China, Kyrgyzstan, and Chile are the leading producers of Mercury in the world.[1]
प्राप्तिस्थानम् ॥ Place of Availability
Native mercury occurs in isolated drops and occasionally in larger fluid masses, usually with cinnabar, near volcanoes or hot springs. It is available generally in small globule form, situated in the deep holes in earth crust. Native mercury is available in USA in California, Almaden (Spain), Peru, Italy, New Zealand, Ukraine, Turkey, Brazil, Columbia, Equador apart from a few other places.[1][2]
Ores of Mercury
Cinnabar, mercury sulfide (HgS), is the chief ore mineral of mercury. It is commonly encountered with pyrite, marcasite, and stibnite in veins near recent volcanic rocks and in hot-springs deposits. The most important deposit is at Almadén, Spain, where it has been mined for 2,000 years.[1]
- Sulphide Ores
- Cinnabar (HgS) or Hingula
- Metacinnabar (β-HgS)
- Living Stonite (HgS 2Sb2S3)
- Chloride Ore
- Calomel (Hg2Cl2)
- Oxide Ore
- Monotroydite (HgO)
रासभेदाः ॥ Types of Parada
In Rasaratna samucchaya,[8] we find the following synonymous terms Rasa, Rasendra, Suta, Parada and Mishraka described as the five kinds of Parada.
रासो रसेन्द्रः सूतश्च पारदो मिश्रकस्तथा । इति पञ्चविधो जातः क्षेत्रभेदेन शम्भुजः॥ (Rasa. Ratn. Samu. 1.68)[8] rāsō rasēndraḥ sūtaśca pāradō miśrakastathā | iti pañcavidhō jātaḥ kṣētrabhēdēna śambhujaḥ||
Their qualities are also well described in the above text (Rasa. Ratn. Samu. 1.69-75)[8]
| S. No | Types of Mercury | Color | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rasa (रसः) | Rakta varna (Red) | Devoid of all impurities, rejuvenative. Devatas overcome aging and remain eternal. Rare in existence. |
| 2 | Rasēndraḥ (रसेन्द्रः) | Syava varna (Grey) | Devoid of all impurities, rejuvenative, rooksha and capable of quick movement. Nagadevatas use this to remain young and deathless. Rare in existence. |
| 3 | Sūta (सूतः) | Peeta varna (Yellowish orange) | It contains some impurities and needs 18 samskaras to purify it. Consuming the purified Suta makes the body strong like a metal. |
| 4 | Pārada (पारदः) | Sveta varna (White) | It cures all diseases and is very fluid-like. It contains some impurities and needs 18 samskaras to purify it. Consuming the purified Suta makes the body strong like a metal. |
| 5 | Mishraka (मिश्रकः) | Mayura chandika chaya (mixed color) | Contains impurities, needs 18 samskaras |
Acharya Saranagadhara mentions synonyms classified based on their name, form, action, metallic state, etc. Synonyms related to
- Dehavada include Amritam, Dehada, Rasayanasreshta, Parada, Mrityunashana, Jaitra etc.
- Dhatuvada include Divyarasa, Rasa, Rasendra, Rasaraja, Suta, Sutaraja, Siddhadhatu, Rasadhatu etc.
- Darshanikata include Jiva, Divya, Achinta etc.
- Gunas include Ananta, Amara, Kalikanta, Sukshma, and Soubhagya
- Svarupa include Chanchala, Mahateja, Chamara etc.
- Daivatva include Trinetra, Harabeejam, Shiva, Shivaveerya, Skanda, Harateja, Rudraja, Deva etc.
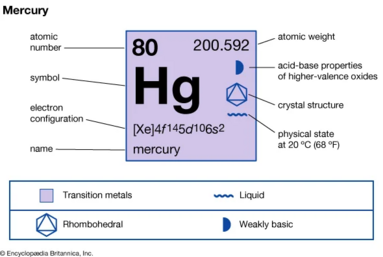
Properties and Uses of Parada
Physical Properties
Mercury (Hg) has a unique combination of physical properties. Its low melting point and boiling point, high specific gravity (13.5 grams per cubic centimetre), uniform volume expansion over the entire range of temperatures in its liquid state, and high surface tension (so that it does not wet glass) make it useful for the measurement of temperature in thermometers and of pressure in barometers and manometers. In addition, the high electrical conductivity of liquid mercury has led to its use in sealed electric switches and relays, industrial power rectifiers, fluorescent and mercury-vapour lamps, mercury cell batteries, and as moving cathodes in the large-scale production of chlorine and caustic soda.
| atomic number | 80 |
|---|---|
| atomic weight | 200.592 |
| State at 20 °C | Liquid |
| Solidifying point | 39 °C |
| melting point | −38.829°C, (−37.892°F) |
| boiling point | 356.619°C, (673.914°F) |
| Specific Gravity | 13.6 grams/cm3 |
| oxidation states | +1, +2 |
| electron configuration | [Xe] 4f145d106s2 |
Pharmacological Properties
Most of Rasa formulations have mercury as an important ingredient. Unpurified mercury has many toxic effects such as severe gastrointestinal irritations, peripheral circulatory collapse, metallic taste in mouth, excessive salivation, inflammation of gums, etc. Almost all classical texts related to Rasa Shastra (Ayurveda pharmaceutics for metalo-mineral preparations) have emphasized Parada Shodhana (purifying process of mercury) but with a variety of methods. These methods need to be revalidated with comprehensive methodology to develop its standard operative procedure (SOP), because standardization of the drugs is very crucial to ensure quality, efficacy, and reproducibility. Hence, Shodhana (purifying process), Mardana (trituration), Marana (incineration), Jarana (polling), Murchchna (process to put in disease curing capacity), etc., with herbomineral drugs are to be carried out as appropriate to receive the therapeutic benefits of Parada.[10]
Although mercury compounds are regarded as poisonous, cinnabar (mercuric sulphide) is subjected to eighteen complex processes called samskāras, including rubbing with various medicinally efficacious plant juices and extracts, incorporation of sulphur, mica, certain alkaline substances, etc. The resulting mercury compound was then declared fit for consumption and believed to lead to the body’s rejuvenation.
Uses of Mercury
Based on the utility of drugs in processing of Parada, they are classified in to Maharasa, Uparasa and Sadharana rasa. Maharasas have wide therapeutic utility and they are used / prescribed along with parada. They are also utilized in various samskaras of parada. Mercurial preparations are used in Pandu (anemia), Shwasa (dysapoea), Kasa (cough), Kamala (jaundice), Jwara (fever), Shula (spasmodic pain), Mutrakriccha (nephritis), Vamana (vomiting), Udara Pida (acute abdominal pain), Krimi Dosha (worm infestation), Atisara (diarrhea), etc.[11]
पारदस्य नेसर्गिका दोषाः ॥ Doshas or Impurities of Parada
According to Rasatarangini, Parada
नागवङ्गौ वह्निमलौ चापल्यं गरलं गिरिः । असह्याग्निश्च विज्ञेयो दोषा नैसर्गिका रसे ॥७॥ nāgavaṅgau vahnimalau cāpalyaṁ garalaṁ giriḥ | asahyāgniśca vijñēyō dōṣā naisargikā rasē ||7||
नागाद् व्रणं भवेत्कुष्ठं वङ्गात्तापोऽग्निदोषतः । मलाज्जड्यं तु चापल्याद् बोजनाशो विषान्मृतिः ।॥८॥ nāgād vraṇaṁ bhavētkuṣṭhaṁ vaṅgāttāpō’gnidōṣataḥ | malājjaḍyaṁ tu cāpalyād bōjanāśō viṣānmr̥tiḥ |||8||
गिरेः स्फोटोऽथ मोहश्च ह्यसह्याग्नेः प्रजायते । एतैर्दोषैर्विहीनञ्च रसेन्द्रमिह योजयेत् ॥ ९॥ girēḥ sphōṭō’tha mōhaśca hyasahyāgnēḥ prajāyatē | ētairdōṣairvihīnañca rasēndramiha yōjayēt || 9|| (Rasa. Tara. 5.7-9)[7]
Intrinsically, Parada contains eight doshas namely, नाग (naga), वङ्ग (vanga), वह्नि (vahni), मल (mala), चापल्य (chapala), विष (visha), गिरि (giri), असह्याग्नि (asahyagni)
Though many Doshas are attributed to Mercury, Naga (Lead), Vanga (Tin) Doshas are considered the major ones.
Mercury Poisoning
In the early 1950’s fishermen and their families around Minamata Bay in Japan were stricken with a mysterious neurological illness. The disease produced progressive weakness of the muscles, loss of vision due to visual cortex lesions, impairment of cerebral functions especially cerebellar ataxia, eventual paralysis and in some cases coma and death. It was soon observed that Minamata seabirds and household cats, which like the fisherfolk subsist mainly on fish, showed signs of the same disease. This led to the discovery of high concentrations of mercury compounds in fish and shell-fish taken from the bay, and the source of mercury was traced to the effluent from a factory.
Since then there have been several other alarming incidents in other parts of the world: Iraq, Pakistan, Guatemala, Sweden, North America and Canada. Mankind has become acutely fearful of mercury in the environment. The alarm is understandable; mercury or quicksilver has always been regarded as being magical, in part because of its unique property as the only metal that is a liquid at ordinary temperature. The uncompounded element in liquid form is not a poison; a person could swallow upto a pound or more of quicksilver with no significant adverse effects. Certain compounds of mercury have been used safely for thousands of years. There is evidence that cinnabar or mercuric sulphide (HgS) was mined in China, Asia Minor, the Cyclades and Peru at least two or three millennia ago. Hippocrates is believed to have prescribed mercury sulphide as a medication.
By the Middle Ages, when alchemists had synthesized chlorides, oxides, and various other inorganic compounds and mixtures of mercury, its use in medications began to spread. Calomel (mercurous chloride, HgCl) came into wide use as a cathartic, and in the 16th Century mercury compounds were introduced as a treatment for syphilis.
In agriculture, corrosive sublimate (HgCl2) is used to disinfect seeds and to control many diseases of the tubers, corns and bulbs (including potatoes), and also to protect a number of vegetable crops. Corrosive sublimate is toxic, causing corrosion of the gastrointestinal tract leading to bloody diarrhoea, injury to the kidneys, ultimately leading to death from renal failure.
What causes concern to environmentalists at present is the alkyl compounds—methyl and ethyl mercurials. The alkyl mercury compounds can cause congenital mental retardation, cerebral palsy and chromosomal abnormalities. The chemical basis for these effects is mercury’s strong affinity for sulphur, particularly for the sulphydryl (S-H) groups in proteins (for which arsenic and lead have a similar affinity). Bound to proteins in a cell membrane, the mercury may interfere with a number of enzymes systems essential to cellular metabolism and alter the distribution of ions, change electrical potentials and thus interfere with the movements of fluid across the membrane. There are also indications that binding of mercury to protein disturbs the normal operation of structures, such as mitochondria and lysosomes within the cell.[12]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Britannica, T. Editors of Encyclopaedia. "mercury." Encyclopedia Britannica, August 20, 2024. https://www.britannica.com/science/mercury-chemical-element.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Sekhar Reddy, P. A textbook of Rasashastra. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Orientalia (pp.72-)
- ↑ Bhinde SS, Patgiri BJ. Quantification of mercury after Samanya Shodhana (purifying process): A preliminary analysis. J Drug Res Ayurvedic Sci 2022;6:65-71.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Ram, Guttikonda S., Mahadev, B., & Chalapathi, R. (2016). A LITERARY REVIEW ON MERCURY W.S.R. TO ITS MEDICINAL ASPECT. AYUSHDHARA, 1(1). Retrieved from https://ayushdhara.in/index.php/ayushdhara/article/view/172
- ↑ Dadu, Vaibhav. (2016) Philosophical Tenets of Vaiseshika and the fundamentals of Ayurveda World Journal of Pharmaceutical
- ↑ Srinivasan, Sharada and Ranganathan, Srinivasa. (2013) Minerals and Metals Heritage of India. Bangalore:National Institute of Advanced Studies.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 Kashinath Shastri (1986 reprint) ed., Ras Tarangini Of Sadananda Sharma With Prasadani Explanation Of Haridatt Shastri And Ras Vigyan Hindi Tika Of Dharmanand Shastri. Delhi: Motilal Banarsidas (pp. 71- )
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 Shankarlal Harishankar, (2019) ed. Rasaratna Sammuchhaya by Acharya Vagbhata Bombay: Khemraj Srikrishnadas Prakashan
- ↑ https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/80/mercury
- ↑ Bhinde SS, Patgiri BJ. Quantification of mercury after Samanya Shodhana (purifying process): A preliminary analysis. J Drug Res Ayurvedic Sci 2022;6:65-71.
- ↑ Sarkar, P.K., Das, Sanjita, Prajapati, P. K. (2010) Ancient concept of metal pharmacology based on Ayurvedic Literature Ancient Science of Life, Vol. 29, 4; pp1-6
- ↑ Lele, R. D. (2012) History of Medicine in India. New Delhi: National Centre of Indian Medical Heritage, Ministry of AYUSH, GOI